Revit and Sustainability: Designing Green Buildings with BIM
Tweet
Architects and designers play a crucial role in sustainability in an era where environmental consciousness is increasingly important. A powerful tool for integrating sustainability into the design process is Building Information Modeling (BIM) software, such as Revit. Architects can design sustainable buildings using Revit's capabilities to minimize environmental impact, enhance energy efficiency, and promote environmental sustainability.
Energy Analysis and Performance
Designers can evaluate the energy efficiency of their building concepts using the energy analysis tools provided by Revit. In order to maximize energy efficiency, architects can analyze various design approaches and make educated selections by modeling energy use, heating, cooling, and day-lighting.
The software offers insightful information regarding the effects of numerous design components, including insulation, glazing, HVAC systems, and the incorporation of renewable energy sources. With the use of this analysis, architects may pinpoint areas for development and create structures that use less energy, emit less greenhouse gasses, and improve the built environment.
Passive Design Strategies
Sustainable design practices include passive design techniques, which make use of environmental factors to enhance building performance. Architects may successfully apply passive design principles to their projects thanks to Revit. Designers can optimize a building's orientation, form, and fenestration to maximize daylighting and reduce heat gain by emulating solar exposure, shade, and natural ventilation.
Rapid simulations and iterations are made possible by Revit's parametric modeling features, ensuring that the design achieves the best passive design performance. The use of passive design techniques can dramatically lower energy requirements while improving occupant comfort.
Material Selection and Life Cycle Assessment
Life cycle analysis and material selection are made easier by Revit. The software enables architects to specify material characteristics and evaluate how various materials affect the environment throughout the course of their lives. When choosing materials, designers can make educated choices by taking into account aspects like embodied energy, carbon footprint, and recyclability.
Architects can give environmental options priority by using the library of sustainable materials in Revit. This comprehensive method of material choice makes sure that the building's construction and use leave as little of an ecological imprint as possible.
Water Efficiency and Rainwater Harvesting
Global water shortage is a problem, and green buildings work to reduce water use and support effective water management. By incorporating elements like low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting systems, and grey-water recycling, Revit's tools let architects design water efficient buildings.
Designers can maximize a building's water efficiency by modeling water use and examining the effects of various water saving techniques. The selection of appropriate water conservation solutions is made easier with the use of Revit's complete analysis capabilities, which supports sustainable water management.
Collaborative Design and Integration
The integration of sustainable design practices across disciplines is made easier by Revit's collaborative design capabilities. BIM makes it possible for consultants, engineers, and architects to collaborate in a coordinated setting while exchanging knowledge and improving a building's sustainability performance.
Revit strengthens communication and facilitates the seamless integration of sustainable design solutions by centralizing project data and establishing a shared platform for collaboration. This collaborative method makes sure that sustainability factors are taken into account from the beginning of design, leading to more comprehensive and efficient green structures.
Building Performance Monitoring
The possibilities of Revit go beyond the design stage and into the building's operating life. Revit offers ongoing building performance monitoring by interfacing with building management systems. Architects may evaluate the actual energy consumption, indoor air quality, and occupant comfort thanks to this real time feedback.
Designers can pinpoint areas for improvement and put strategies in place to maximize building performance by analyzing this data. The building's sustainability features may be regularly monitored and adjusted, ensuring that they perform at their best for the duration of their useful lives.
Day-lighting Analysis and Optimization
Using the day-lighting analysis tools in Revit, architects may assess how natural light is distributed across a building. Designers can maximize the amount of natural light that enters a space and lessen the need for artificial lighting by modeling various fenestration designs, interior layouts, and shading mechanisms. By accurately visualizing and analyzing daylight levels, Revit enables architects to design rooms that improve occupant well being, conserve energy, and rely less on electric lighting.
Renewable Energy Integration
The incorporation of renewable energy systems into architectural designs is made easier by Revit. Architects can use Revit to evaluate the viability and performance of renewable energy technology, including solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal systems.
Designers can maximize the energy generation potential of renewable energy systems by optimizing the placement and scale of these systems based on analysis of sun exposure, wind patterns, and geological data. Buildings that produce clean energy and less reliance on fossil fuels can be made with the help of Revit's ability to analyze and simulate the integration of renewable energy sources.
Green Building Certifications
For green building rating systems like LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) or BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method), Revit facilitates the documentation and certification process. Using the program, architects can keep track of and record the sustainable design elements they use in their projects, ensuring that they meet certification standards.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Archistudent
By integrating Revit with various rating systems, architects can more easily show the environmental performance of their projects and the certification process is made simpler.
Life-Cycle Cost Analysis
Using Revit, architects can do life cycle cost analyses, which assess the financial viability of sustainable design choices over the course of a building's life cycle.
Designers can combine upfront investment with long term financial gains by taking into account elements including initial building costs, maintenance costs, energy savings, and operational costs. The investigation of various design scenarios is made possible by Revit's parametric modeling features, helping architects find sustainable, affordable solutions.
Green Roof and Landscape Integration
The integration of green roofs and landscapes, which promote sustainability and the environment, is possible using Revit's modeling tools. Within the software, architects can create and replicate vegetated roofs, rain gardens, and other types of green infrastructure.
Designers may construct green areas that improve the sustainability performance of the building while offering ecological and aesthetically pleasing benefits by analyzing their impact on storm-water management, energy efficiency, and biodiversity.
Occupant Well-being and Comfort
With the use of Revit, architects may maximize occupant comfort and well-being using environmentally friendly design principles. The health and productivity of occupants can be prioritized in design by emulating indoor air quality, thermal comfort, and acoustics. With the use of Revit's analytical tools, architects may assess insulation, soundproofing, and ventilation systems to make sure that the indoor environment of the building fosters a high quality and comfortable experience for its occupants.

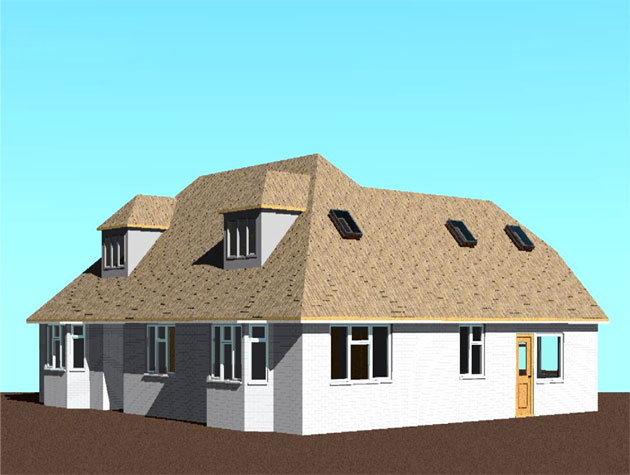
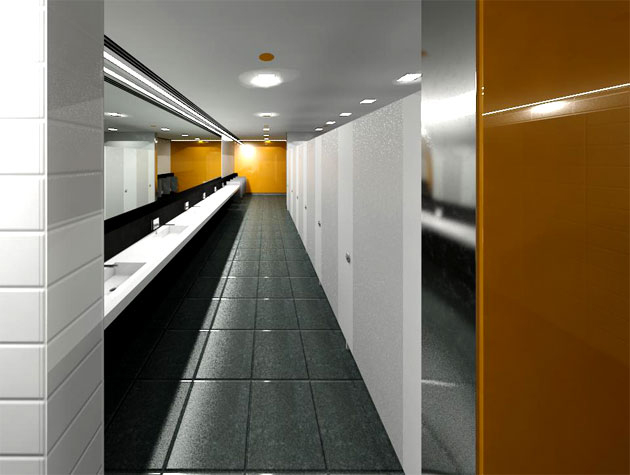
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !