Revit 101: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Tweet
IArchitects, engineers, and construction professionals have transformed the way they design and collaborate on building projects with Revit, developed by Autodesk. Revit's intuitive interface and robust set of tools make it ideal for designing and documenting buildings holistically.
Revit's fundamental concepts must be understood before diving into its intricacies. A BIM represents the physical and functional characteristics of a building digitally. In a collaborative environment, Revit creates a virtual model of the project using BIM principles.
Navigating the Interface
A user friendly interface, including the Ribbon, Quick Access Toolbar, Project Browser, and Properties Palette, greets users when Revit first launches. It is essential to comprehend these interface elements in order to navigate the software quickly and access all of its features.
Building Elements and Families
The basic pieces that make up a project in Revit are called building elements. Walls, doors, windows, roofs, and other components are among these. Users of the software can drag and drop these elements into the project from a large library of premade families. Custom families can also be made to satisfy particular design specifications.
Creating and Modifying Elements
A variety of tools are available in Revit to create and alter architectural components. Users are able to precisely sketch and alter floor plans, elevations, and sections. The software's parametric features make it simple to modify pieces, facilitating speedy design iterations. Users can modify the project's dimensions, components, and other attributes to improve its appearance and functionality.
Working with Views and Sheets
Floor Plans
Floor plans give a bird's-eye view of the building and show how the walls, doors, windows, and other components are arranged. Users can develop and alter floor plans for various building levels, enabling careful planning and coordination.
Elevations and Sections
Sections offer cut-through views of the inside while elevations display the building's external facades from a vertical perspective. These views enable precise coordination and details by aiding in the visualization and communication of design intent.
3D Views
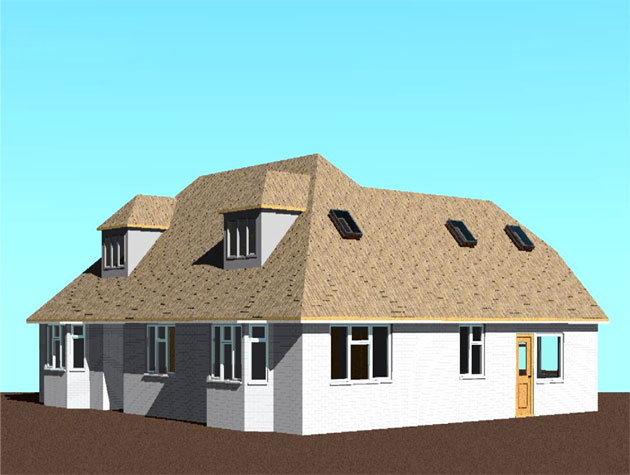
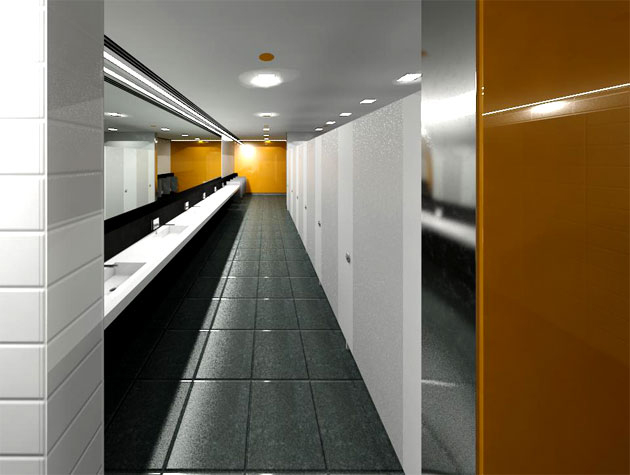
A three dimensional representation of the building is provided by 3D views, allowing people to examine the design from various perspectives. Users can move around the 3D model, add materials, and produce realistic renderings to show clients and stakeholders the project.
Schedules
The data gathered from the project, such as quantities, materials, and dimensions, is extracted into schedules in Revit. Users can make plans to keep track of various project components, produce material take-offs, and guarantee proper documentation.
Sheets
To compile views and make drawing sets, use sheets. Users can create professional-looking construction papers by arranging numerous views on a sheet, adding annotations, dimensions, and title blocks.
Collaboration and Coordination
Worksharing
The worksharing feature of Revit enables many users to work together on a project at once. Users have the ability to make local copies of the central model, edit them, and then sync their changes to the central model to provide smooth collaboration and version control.
Collaboration Tools
Tools for collaborating and communicating with project team members are provided by Revit. Within the platform, users can post comments, assign tasks, and monitor project progress, easing communication and enhancing coordination.
Clash Detection
The clash detection function in Revit aids in locating conflicts between various building systems, including mechanical, electrical, and structural elements. Conflicts can be found and resolved before construction begins, preventing expensive rework and conserving time and money.
Visualizing and Analyzing Designs
Rendering
Users can produce high quality, lifelike images and animations of their designs using the rendering features in Revit. Users can use materials, lighting, and environmental effects to create visually appealing presentations for clients and promotional materials.
Walkthroughs
Users of Revit's walkthrough tool can create animated tours of their designs, giving stakeholders the impression that they are actually walking around the project. Walkthroughs provide users a more complete grasp of the design and aid in spotting any problems or room for improvement.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: ArchAdemia
Energy Analysis
Users can assess the energy efficiency of their designs using the energy analysis tools that Revit provides. Users can optimize the building's energy efficiency and sustainability by modeling various scenarios and examining energy consumption.
Expanding Functionality with Add-ins
The use of add-ins can further increase Revit's capability. These third party developed plug-ins provide specialized tools and capabilities to improve processes and take care of certain project requirements. Users have a wide choice of alternatives to enhance their Revit experience thanks to add-ins, which can include structural analysis tools and cutting edge rendering engines.
Continued Learning and Resources
Revit needs ongoing research and study, just like learning any other piece of software. To help beginners on their way, Autodesk offers thorough documentation, tutorials, and user forums. There are also numerous online training courses and programs available to further develop expertise and understanding in Revit.

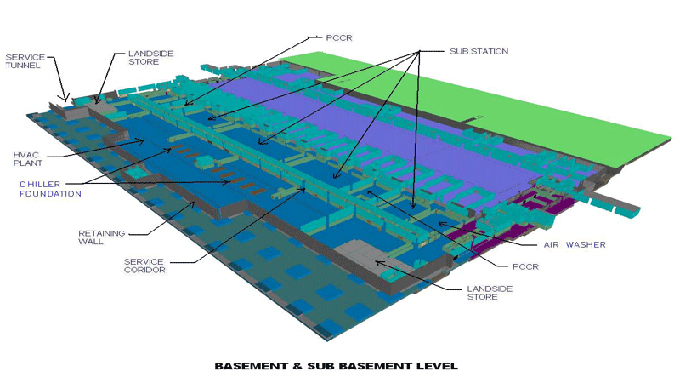
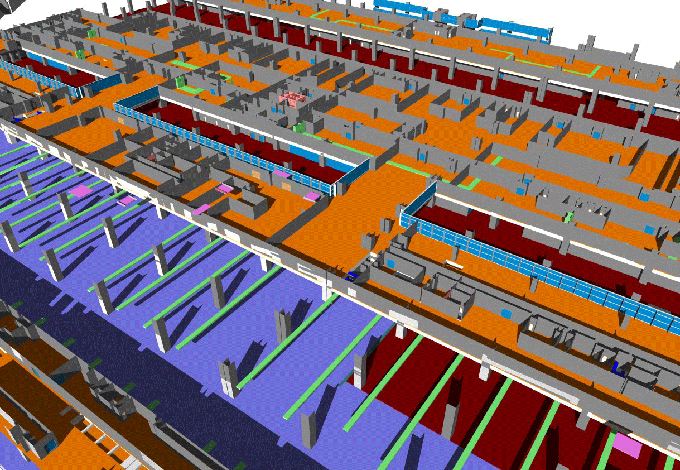
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !