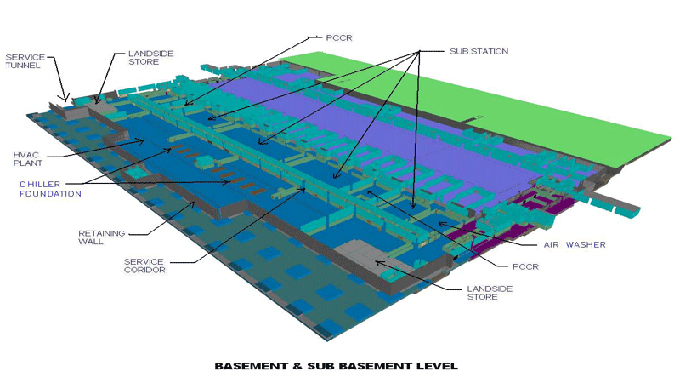
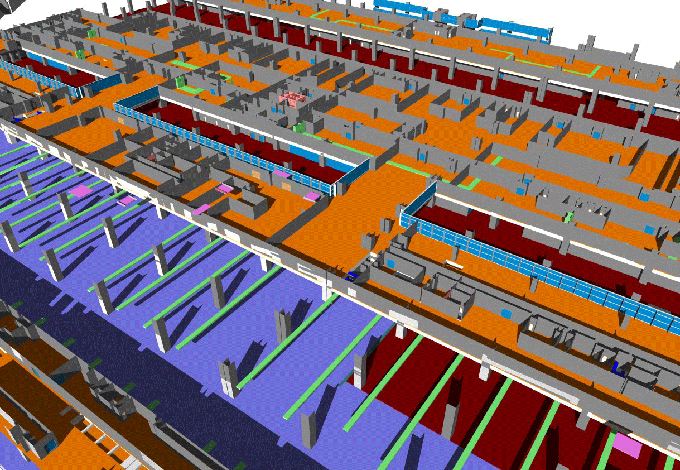
Revolutionizing Event Management: Harnessing the Power of BIM
Tweet
In the ever-evolving landscape of event management, staying ahead of the curve is essential for delivering exceptional experiences. One transformative technology making waves in the industry is Building Information Modeling (BIM).
Traditionally associated with architecture and construction, BIM is now proving to be a game-changer for event managers, offering innovative solutions for planning, designing, and executing events.
Understanding Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Before delving into the specific applications for event management, it is crucial to understand the fundamentals of Building Information Modeling (BIM).
BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure. It goes beyond traditional 2D drawings, incorporating 3D models enriched with data and information about every element within the structure.
Key components of BIM include
1. 3D Models: Detailed, three-dimensional models provide a comprehensive view of the physical space, allowing for a more realistic representation.
2. Data Integration: BIM integrates a wealth of information associated with each element in the model. This can include dimensions, materials, costs, schedules, and more.
3. Collaboration: BIM facilitates collaboration among stakeholders by providing a centralized platform for sharing and accessing project information.
4. Lifecycle Management: BIM supports the entire lifecycle of a project, from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
The Role of BIM in Event Management
Event managers are constantly faced with the challenge of creating memorable and seamless experiences for attendees. From corporate conferences to music festivals, the success of an event hinges on meticulous planning and execution. Here's how event managers can leverage BIM to elevate their work:
1. Venue Selection and Design
a. Virtual Venue Tours: Event managers can use BIM to create virtual tours of potential venues. This allows clients and stakeholders to explore the space remotely, gaining a realistic understanding of the layout, dimensions, and ambiance.
b. Spatial Planning: BIM enables precise spatial planning, helping event managers optimize the use of available space. It allows for the visualization of seating arrangements, exhibit layouts, and traffic flow, ensuring efficient use of every square foot.
c. Customization and Personalization: Event managers can collaborate with architects and designers using BIM to customize and personalize event spaces. Whether it's adjusting lighting schemes or experimenting with different stage setups, BIM provides a platform for creative exploration.
2. Logistics and Infrastructure Planning
a. Equipment Placement: BIM allows event managers to strategically place equipment, such as audio-visual systems, lighting rigs, and stages. This ensures optimal sightlines, acoustics, and overall event flow.
b. Resource Optimization: By modeling the venue and its infrastructure in BIM, event managers can optimize resource allocation. This includes managing power distribution, coordinating with vendors, and streamlining logistical processes.
c. Risk Assessment: BIM's data-rich models enable event managers to conduct thorough risk assessments. From identifying potential bottlenecks to assessing emergency evacuation routes, BIM contributes to comprehensive event safety planning.
3. Budgeting and Cost Estimation
a. Accurate Cost Estimates: BIM's data integration capabilities extend to cost estimation. Event managers can generate accurate cost estimates by associating cost data with each element in the BIM model, helping in budget planning and client communication.
b. Resource Optimization: By visualizing the event space in detail, event managers can identify areas where costs can be optimized. This includes efficient use of space, strategic placement of elements, and informed decision-making regarding materials and infrastructure.
4. Collaboration and Communication
a. Centralized Collaboration: BIM serves as a centralized platform for collaboration among various stakeholders, including architects, designers, vendors, and clients. Real-time updates and changes are reflected in the model, fostering seamless communication.
b. Design Iterations: Event managers can work closely with designers to iterate through different design concepts using BIM. This iterative process allows for quick adjustments and refinements based on feedback, ensuring that the final design aligns with the client's vision.
c. Client Visualization: BIM's visual representation is a powerful tool for client communication. Event managers can use the 3D model to help clients visualize the proposed event space, making it easier for them to provide feedback and make decisions.
5. Construction and On-site Management
a. Construction Coordination: For events involving temporary structures, such as stages and booths, BIM aids in coordinating construction activities. It provides a clear roadmap for on-site teams, minimizing errors and delays.
b. On-site Modifications: During the event setup phase, last-minute changes are not uncommon. BIM allows for quick adjustments and modifications on-site, ensuring that changes are seamlessly integrated into the overall plan.
c. Real-time Updates: BIM's cloud-based platforms enable real-time updates and synchronization. This is particularly beneficial for on-site management, ensuring that everyone involved is working with the latest information.
6. Post-Event Analysis and Documentation
a. As-Built Documentation: BIM supports the creation of as-built documentation, providing an accurate record of the event space after setup. This documentation can be valuable for future events or for conducting post-event analyses.
b. Performance Evaluation: Event managers can use BIM data to evaluate the performance of different event elements. This includes analyzing attendee flow, identifying popular areas, and assessing the success of specific design choices.
c. Continuous Improvement: By leveraging post-event data and feedback, event managers can continuously improve their processes. BIM becomes a valuable tool for refining event strategies and enhancing future planning.
Implementing BIM in Event Management: Best Practices
To effectively incorporate BIM into event management processes, event managers should follow these best practices:
1. Invest in Training
Ensure that your team is well-trained in using BIM software. Familiarity with the tools and features is essential for maximizing the benefits of BIM in event management.
2. Collaborate from the Beginning
Encourage collaboration between event managers, designers, architects, and other stakeholders from the project's inception. This collaborative approach ensures that everyone's input is considered during the planning and design phases.
3. Utilize Cloud-Based Platforms
Opt for BIM platforms that offer cloud-based collaboration. This ensures that stakeholders can access the most up-to-date information from anywhere, facilitating remote collaboration and real-time updates.
4. Integrate BIM with Project Management Tools
Integrate BIM tools with project management software to streamline workflows. This ensures that BIM data is seamlessly integrated into overall project planning and execution.
5. Establish Clear Protocols
Define clear protocols for how BIM data will be shared, updated, and accessed by different stakeholders. Establishing these protocols early on contributes to a more efficient and organized workflow.
6. Engage with Experienced BIM Professionals
Collaborate with experienced BIM professionals who can guide your team through the implementation process. Their expertise can help you navigate challenges and fully leverage the capabilities of BIM.
7. Regularly Update BIM Models
Ensure that BIM models are regularly updated to reflect any changes or modifications. This is particularly crucial during the planning and construction phases to maintain accuracy.
8. Encourage Feedback and Iteration
Create a culture of feedback and iteration. Encourage team members to provide input on the BIM models and iterate through different design concepts to find the most optimal solutions.
9. Document Lessons Learned
Document lessons learned from each event. This includes both successes and challenges encountered during the planning and execution phases. Use this documentation to refine processes for future events.
Case Studies: Successful Integration of BIM in Event Management
1. London 2012 Olympic Games
The London 2012 Olympic Games stands as a notable example of successful BIM integration in event management. BIM was used for the planning, design, and construction of various venues. The technology facilitated collaboration among different teams, optimizing spatial planning and ensuring the timely and efficient delivery of the event.
2. World Expo 2015 in Milan
The World Expo 2015 in Milan utilized BIM to plan and execute the event. BIM models were created for various pavilions and infrastructure, allowing for detailed spatial planning, resource optimization, and effective collaboration among stakeholders. The use of BIM contributed to the overall success of the expo.
Challenges and Future Trends
While the integration of BIM in event management brings about numerous benefits, it's essential to be aware of potential challenges and upcoming trends in the field:
Challenges
Cost of Implementation: Implementing BIM requires an initial investment in software, training, and technology infrastructure.
Resistance to Change: Team members may initially resist adopting new technologies, necessitating effective change management strategies.
Complexity of Models: Managing large and complex BIM models can be challenging, requiring skilled professionals and robust hardware.
Data Security Concerns: Storing event-related data in the cloud raises concerns about data security and confidentiality.
Future Trends
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration: The integration of AR with BIM is on the rise, allowing event managers to overlay digital information onto the physical event space for enhanced visualization.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) for Analytics: AI applications in BIM can provide advanced analytics for predicting attendee behavior, optimizing spatial layouts, and enhancing overall event planning.
Increased Mobility: BIM tools are becoming more mobile-friendly, allowing event managers to access and manipulate models on smartphones and tablets, enhancing flexibility.
Sustainability Integration: BIM is increasingly being used to optimize resource use, reduce waste, and enhance the sustainability of events.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: VinZero - Capricot Technologies
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has evolved from its roots in architecture and construction to become a powerful tool for event managers seeking to revolutionize their approach to planning and execution. By harnessing the capabilities of BIM, event managers can optimize spatial planning, enhance collaboration, and deliver exceptional experiences for attendees.
The integration of BIM in event management is not without its challenges, but the potential benefits far outweigh the drawbacks. With careful planning, training, and a commitment to embracing technological innovation, event managers can position themselves at the forefront of the industry, setting new standards for efficiency, creativity, and success.
As BIM continues to evolve and new technologies emerge, event managers should stay informed about the latest trends and innovations. The future promises even more exciting possibilities for those willing to embrace the transformative power of BIM in shaping the events of tomorrow.

Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !