The Use of BIM for the Role of Forensics
Tweet
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has revolutionized the construction and architecture industries by providing a comprehensive digital representation of building projects. While BIM is traditionally associated with design, construction, and facility management phases, its applications extend beyond these areas.
One such emerging application is the use of BIM in forensics, where it plays a critical role in investigating structural failures, accidents, and defects in buildings and infrastructure. In this article, we will explore how BIM is changing the landscape of forensic investigations, its benefits, challenges, and future prospects.
The Intersection of BIM and Forensics
Defining Forensic Investigation in Construction
Forensic investigation in construction involves the systematic examination and analysis of buildings, infrastructure, and construction processes to determine the causes of structural failures, accidents, defects, or disputes.
It aims to provide evidence for legal or insurance purposes, ensuring accountability and improving safety and quality in the construction industry.
The Evolution of BIM in Forensics
BIM has evolved from being primarily a design and construction tool to becoming a valuable asset in forensic investigations. Some factors are:
A. The increasing adoption of BIM in the construction industry has led to a wealth of digital data related to building projects.
B. The recognition of BIM as an effective means to document, visualize, and analyze complex building structures and systems.
C. The need for accurate and reliable information in forensic investigations to determine liability and ensure fair resolution.
The Benefits of Using BIM in Forensics
Enhanced Data Accessibility
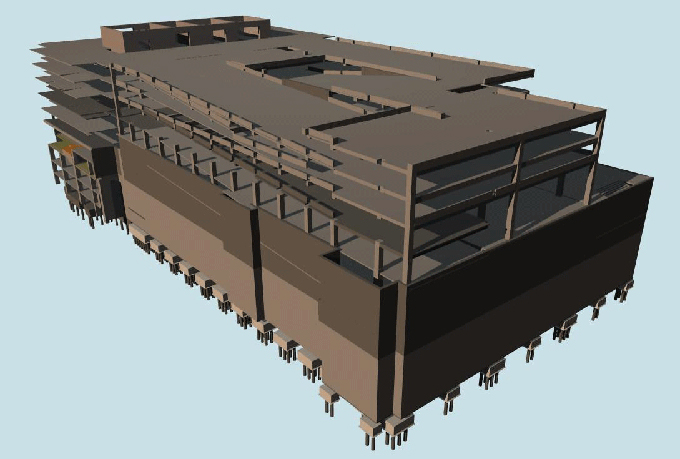
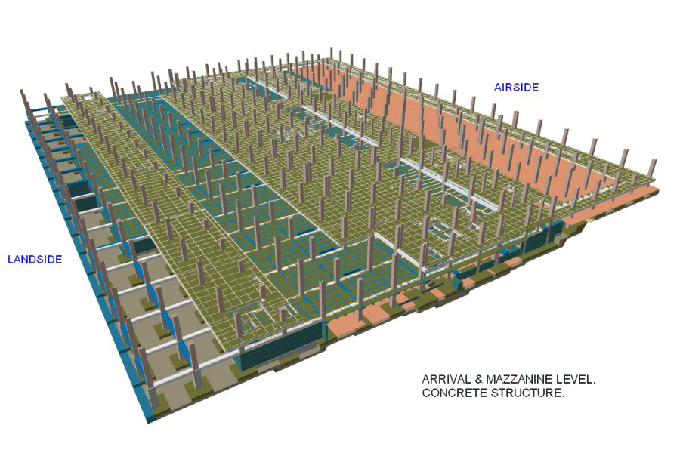
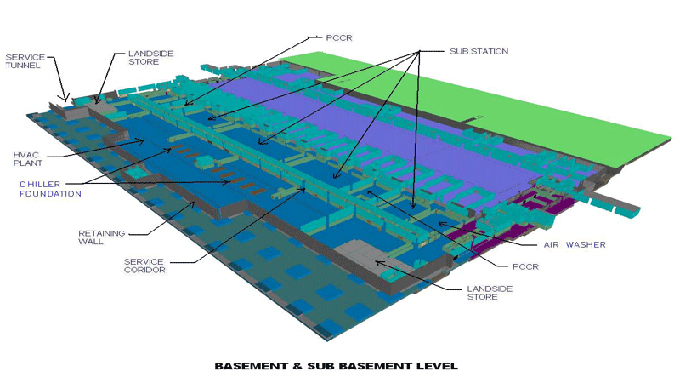
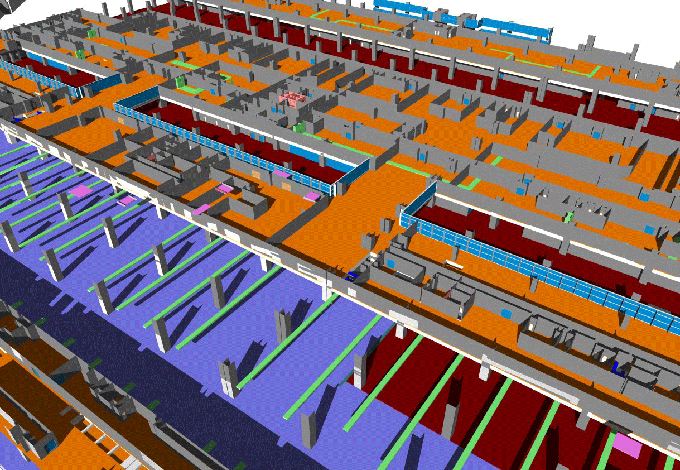
BIM provides investigators with a comprehensive and structured digital record of a building or infrastructure project. This readily accessible data includes design plans, construction schedules, material specifications, and as-built models. Access to this information streamlines the investigation process and allows for in-depth analysis.
Improved Accuracy and Visualization
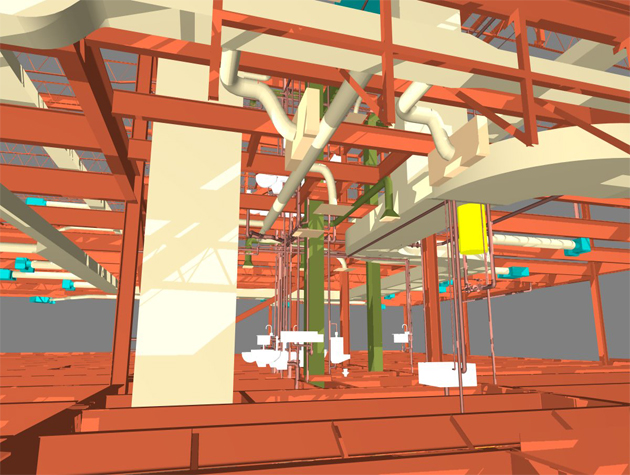
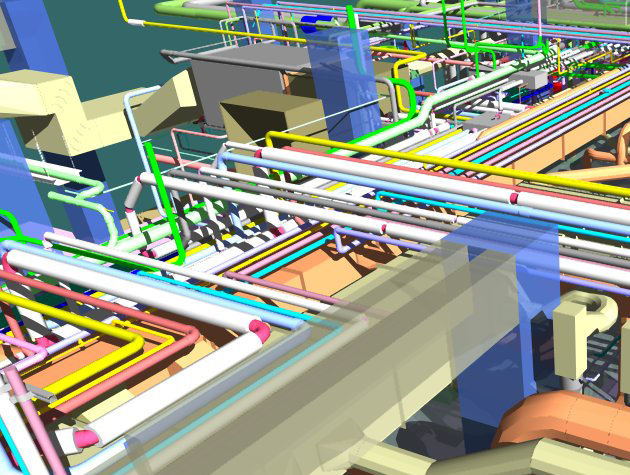
BIM enables investigators to recreate the conditions of the incident or defect accurately. Using 3D models and simulations, they can visualize the sequence of events, potential failure points, and structural behaviour, aiding in root cause analysis.
Time and Cost Savings
Compared to traditional methods of forensic investigation that often involve physical inspections, BIM-based investigations can save significant time and costs. Virtual inspections can be conducted remotely, reducing the need for on-site visits and minimizing disruptions.
Collaborative Analysis
BIM platforms facilitate collaboration among multiple stakeholders involved in the forensic investigation process, including architects, engineers, contractors, and legal experts. This collaborative approach ensures a more comprehensive analysis and a well-rounded understanding of the situation.
Applications of BIM in Forensic Investigations
Accident and Incident Reconstruction
BIM allows investigators to recreate accidents or incidents in a virtual environment, helping determine causative factors. By simulating various scenarios, investigators can identify potential weaknesses in design or construction and pinpoint contributing factors.
Structural and Material Defect Analysis
BIM models serve as invaluable references for examining structural and material defects. Investigators can use these models to compare the actual conditions with the original design intent, identifying deviations and areas of concern.
Fire and Safety Analysis
For fire investigations, BIM provides insights into fire propagation, evacuation routes, and the impact of fire on building structures. This information aids in assessing fire safety measures and determining liability.
Legal and Insurance Documentation
BIM-generated reports, models, and visualizations serve as robust documentation for legal and insurance purposes. They provide clear and compelling evidence that can be used in negotiations, litigation, or insurance claims.
Training and Education
BIM-based forensic investigations provide an excellent opportunity for training and education in the construction and engineering fields. Aspiring professionals can learn from real-world cases by exploring BIM models, conducting virtual investigations, and understanding the complexities of structural failures and defects.
Research and Development
The application of BIM in forensics drives ongoing research and development in both the BIM and forensic investigation fields. Researchers explore new techniques, tools, and technologies to enhance the effectiveness of BIM-based forensic investigations.
International Collaboration
BIM facilitates international collaboration in forensic investigations. Experts from different regions can work together in a shared digital environment, exchange insights, and pool their expertise to solve complex forensic challenges on a global scale.
Challenges and Considerations
Data Quality and Availability
The success of BIM-based forensic investigations depends on the quality and availability of BIM data. Incomplete or outdated models may hinder the accuracy of the analysis.
Privacy and Security
BIM models may contain sensitive information, and their sharing must comply with privacy and security regulations. Protecting data integrity and preventing unauthorized access is crucial.
Technical Expertise
Effective use of BIM in forensics requires a level of technical expertise in both BIM software and forensic investigation techniques. Training and collaboration among experts are essential.
Integration with Existing Processes
Integrating BIM into existing forensic investigation processes may require adjustments and changes to established workflows and methodologies.
Future Trends and Prospects
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
The integration of AI and ML algorithms with BIM can enhance pattern recognition and predictive analysis capabilities in forensic investigations. These technologies can automate data analysis and offer insights that might otherwise be overlooked.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
AR and VR technologies will enable investigators to explore BIM models in immersive environments, enhancing their understanding of complex structural behaviours and contributing to more accurate analysis.
Blockchain for Data Integrity
Blockchain technology can enhance the security and integrity of BIM data, ensuring that the information used in forensic investigations remains tamper-proof and trustworthy.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: 3D Repo
Continuous Improvement
The feedback loop created by BIM-based forensic investigations allows for continuous improvement in construction practices. Lessons learned from forensic cases can be used to inform design and construction standards, leading to safer and more resilient buildings and infrastructure.
Conclusion
The marriage of BIM and forensic investigations represents a significant advancement in the construction industry. BIM's capacity to provide comprehensive, accurate, and collaborative data is transforming the way we investigate structural failures, accidents, and defects.
While challenges related to data quality, security, and expertise persist, the future looks promising with the potential integration of AI, AR, VR, and blockchain technologies. As BIM continues to evolve, it will undoubtedly play an increasingly pivotal role in enhancing safety, accountability, and the overall quality of construction projects.
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !