Unlocking Efficiency: Digitizing Existing Construction with eBIM Models
Tweet
The construction industry is undergoing a digital transformation, and one of the most significant advancements in this shift is the adoption of eBIM (existing Building Information Modeling) models. eBIM is all about bringing digital technology to bear on existing buildings and infrastructure, offering a more efficient and comprehensive way to manage and upgrade them.
Understanding eBIM Models
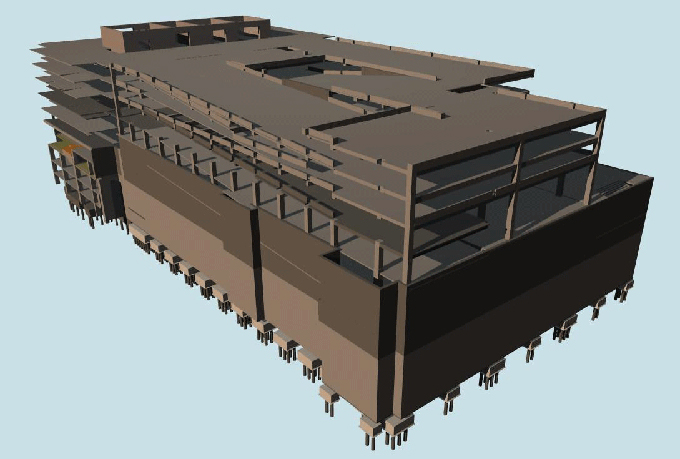
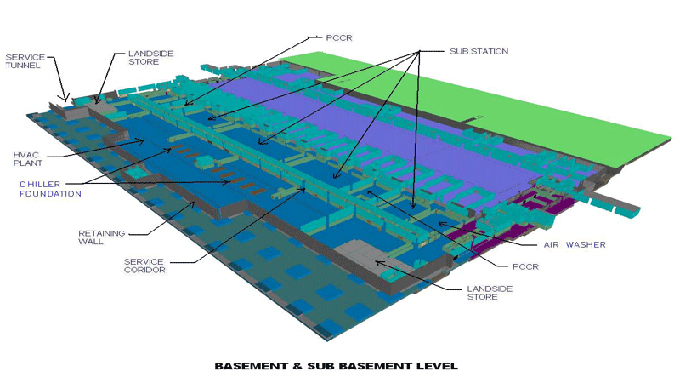
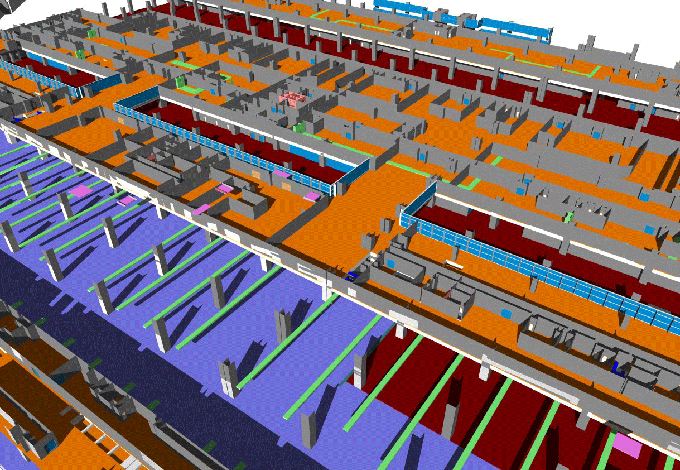
eBIM models, also known as as-is BIM or retro-BIM, involve creating a digital representation of an existing building or infrastructure. These models capture the current state of a facility, incorporating data about its physical and operational characteristics.
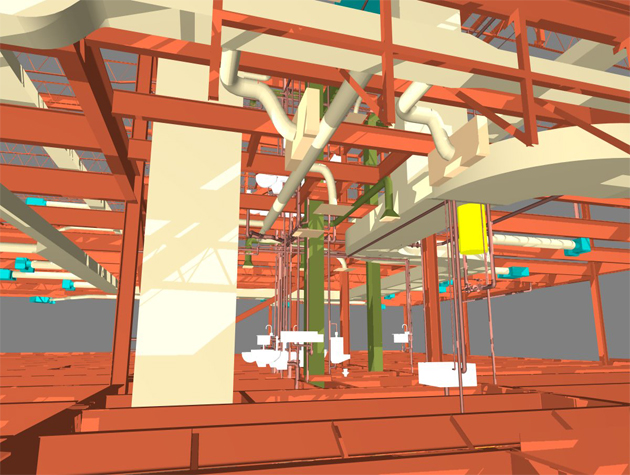
eBIM goes beyond traditional 2D drawings and documents, offering a dynamic and information-rich 3D model that serves as a valuable resource for facility management, renovation, and retrofitting.
The Core Components of eBIM Models:
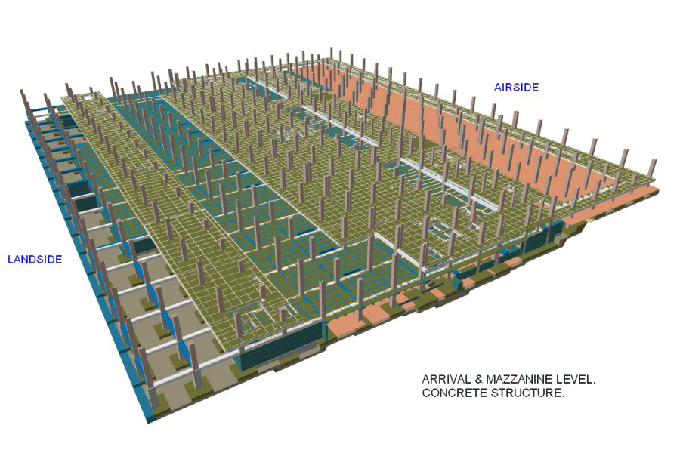
1. Geometry: The 3D geometry of the existing building or infrastructure is accurately represented, capturing its physical form, components, and spatial relationships.
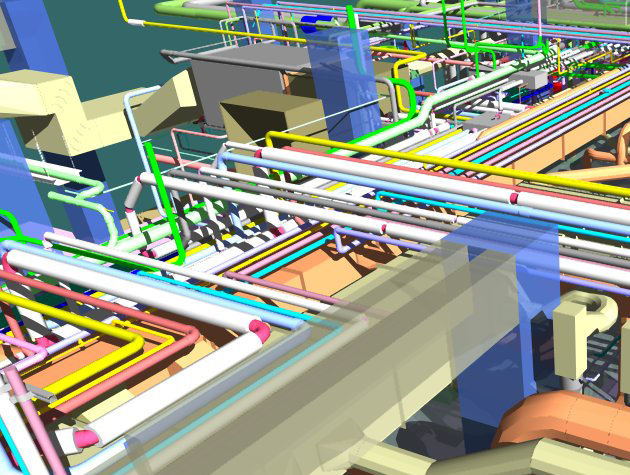
2. Attributes and Data: eBIM models incorporate detailed information about each element within the structure, such as materials, dimensions, maintenance history, and more.
3. As-Built Information: As-built plans and specifications, including changes made during the building's lifecycle, are included in the eBIM model to provide a comprehensive view of the facility.
4. Spatial Data: Geospatial information can be integrated, allowing for precise location mapping within the model.
5. Maintenance and Operations Data: eBIM models can include data related to maintenance schedules, equipment conditions, and operational parameters.
The Benefits of eBIM Models for Existing Construction
Implementing eBIM models for existing construction offers a wide range of benefits, making it a valuable asset for facility owners, managers, and stakeholders:
1. Enhanced Facility Management
eBIM models provide a centralized digital platform to manage and maintain facility assets. Facility managers can access comprehensive information about the building's components, track maintenance schedules, and plan for repairs efficiently.
2. Improved Decision-Making
eBIM models offer valuable insights that aid in decision-making for renovations, retrofits, and upgrades. Stakeholders can visualize the impact of proposed changes and make informed choices.
3. Cost Savings
By facilitating better planning and reducing the risk of unexpected issues during renovations, eBIM models can result in significant cost savings.
4. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
eBIM models enable the identification of opportunities to enhance energy efficiency and sustainability within existing buildings, reducing energy costs and environmental impact.
5. Streamlined Documentation
eBIM models reduce the need for extensive paper documentation and streamline information access. This leads to greater efficiency in day-to-day facility management.
Challenges in Implementing eBIM Models
While eBIM models offer numerous advantages, they also come with certain challenges that need to be addressed:
1. Data Accuracy
Ensuring that the data included in the eBIM model accurately reflects the as-built condition of the facility is a critical challenge. Inaccuracies can lead to costly errors during renovations.
2. Data Integration
Collecting and integrating data from various sources, including historical documents, drawings, and field surveys, can be complex and time-consuming.
3. Cost and Resource Requirements
Creating eBIM models requires an investment in technology, software, and skilled personnel. Smaller organizations may face budget limitations.
4. Legacy Data
Many existing facilities lack up-to-date as-built documentation, which means that retroactive data collection efforts are necessary.
5. Change Management
Implementing eBIM models often involves a change in workflow and processes. Resistance to these changes can be a barrier to adoption.
Best Practices for Implementing eBIM Models
To successfully implement eBIM models for existing construction, consider the following best practices:
1. Clearly Define Objectives
Establish clear objectives for your eBIM project. Determine what specific information and functionality you want from the model to guide the data collection process.
2. Data Collection Plan
Create a comprehensive plan for data collection. This includes identifying data sources, data quality requirements, and a schedule for gathering information.
3. Select the Right Tools
Choose the appropriate software and technology for creating and managing eBIM models. Ensure your team is trained and proficient in using these tools effectively.
4. Standardize Data
Standardize the data structure and format to ensure consistency and compatibility across the model. Implement naming conventions and data management protocols.
5. Quality Control
Implement a rigorous quality control process to verify data accuracy and completeness. Regularly update the model as new information becomes available.
6. Collaborative Approach
Promote collaboration among stakeholders, including facility owners, managers, architects, engineers, and contractors. Encourage open communication to address challenges and opportunities effectively.
7. Change Management
Recognize that the transition to eBIM models may require a shift in organizational culture and workflow. Implement change management strategies to support a smooth transition.
Case Studies: eBIM Success Stories
To illustrate the potential of eBIM models in existing construction, here are two case studies highlighting successful implementations:
Case Study 1: Renovating a Historic Landmark
A historic landmark building required a renovation that aimed to preserve its architectural heritage while upgrading its infrastructure for modern use. The project team created an eBIM model that integrated architectural drawings, structural data, and as-built information.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Parametric Architecture
This comprehensive eBIM model enabled the project stakeholders to plan renovations with a high degree of accuracy, ensuring that the building's historical features were preserved while modernizing its utilities.
Case Study 2: Facility Management for a University Campus
A university campus with multiple buildings faced challenges in efficiently managing its facility assets and maintenance. Implementing eBIM models for each building allowed the facilities team to access up-to-date information about the structures and their systems. This significantly improved facility management, streamlined maintenance, and reduced downtime for repairs.
Conclusion
eBIM models are a game-changer in the construction industry, offering an innovative approach to digitizing existing construction. With their ability to improve facility management, support informed decision-making, and contribute to cost savings and sustainability, eBIM models are poised to play a pivotal role in the future of the built environment.
While challenges exist in implementing eBIM models, careful planning, data accuracy, and change management can help overcome these obstacles. As the construction industry continues to embrace digital transformation, eBIM models are set to become a standard practice for enhancing the efficiency and sustainability of existing buildings and infrastructure.

Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !