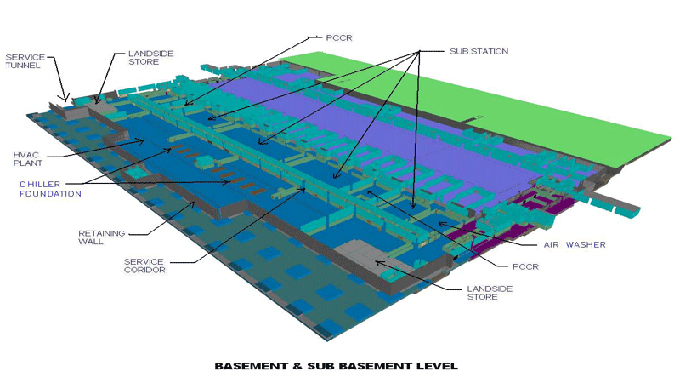
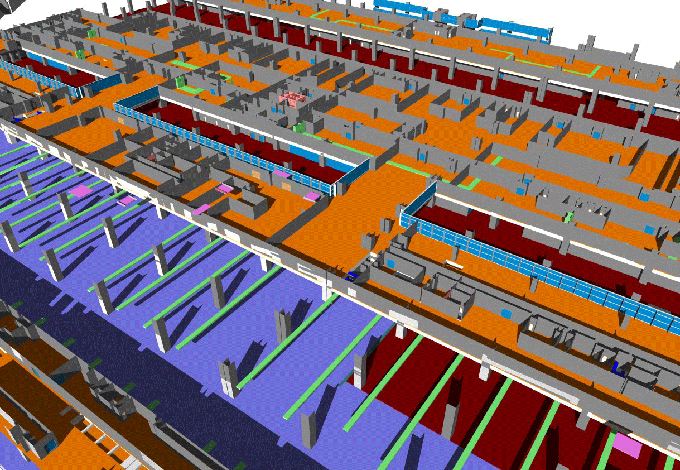
Transforming Construction: The Role of BIM in Empowering Developers and Coders
Tweet
In the ever-evolving landscape of the construction industry, Building Information Modeling (BIM) has emerged as a revolutionary technology that goes beyond traditional 2D design, enabling developers and coders to collaborate seamlessly and enhance project efficiency.
Understanding Building Information Modeling (BIM)
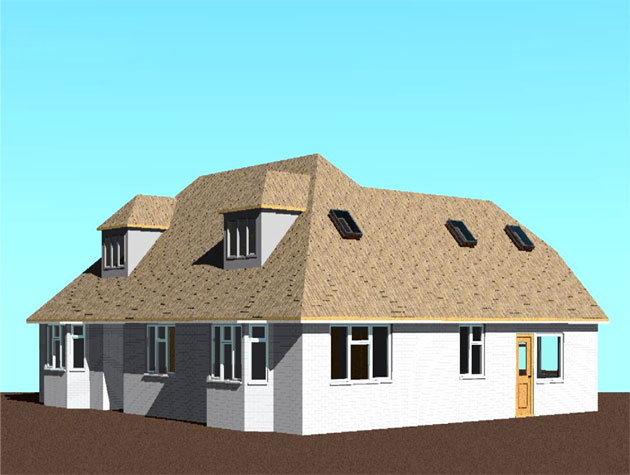
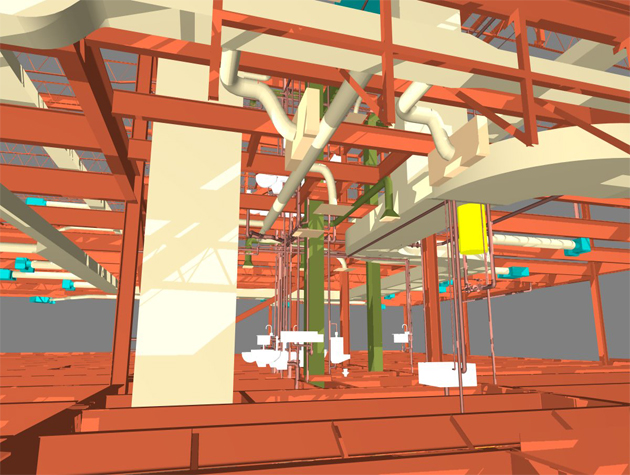
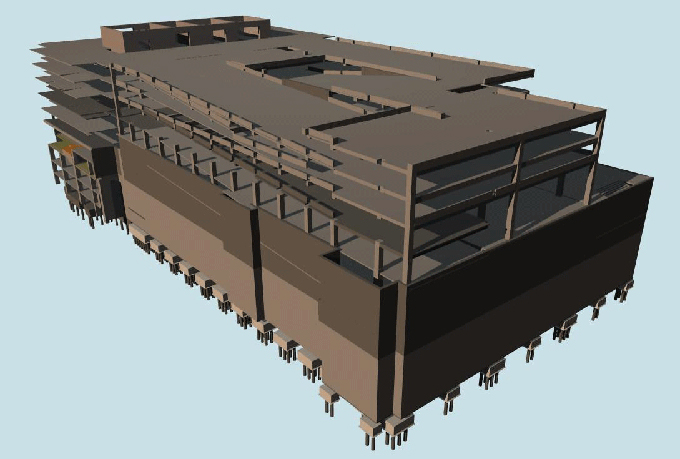
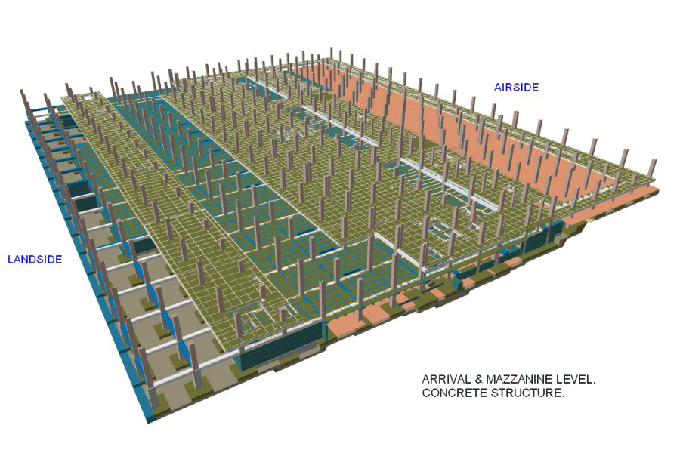
Building Information Modeling is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure. Unlike traditional CAD (Computer-Aided Design), BIM encompasses not only the geometry of the structure but also integrates data about its components and their relationships in a 3D model.
This data-driven approach provides a comprehensive view of a project, facilitating better decision-making throughout its lifecycle.
Enhanced Collaboration and Communication
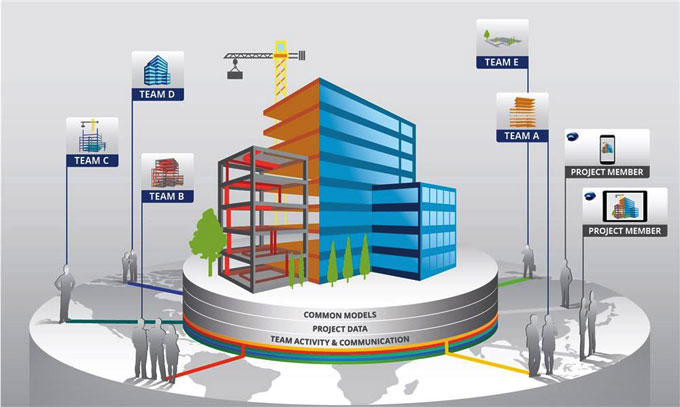
One of the primary advantages of BIM is its ability to break down silos and foster collaboration among various stakeholders, including developers, architects, engineers, and coders. Through a centralized digital model, teams can work concurrently on different aspects of a project, streamlining communication and minimizing errors.
Developers and coders can benefit significantly from this collaborative environment. By having access to a shared digital platform, they can gain insights into the project's overall design and functionality. This collaborative approach ensures that the software and coding align seamlessly with the architectural and engineering elements, reducing the likelihood of errors during implementation.
Streamlined Project Management
BIM plays a pivotal role in project management by providing a centralized repository of information. Developers and coders can access this repository to understand the project's requirements, timelines, and dependencies. This transparency allows for better planning and coordination, reducing the risk of delays and cost overruns.
Moreover, BIM enables the creation of accurate and realistic project schedules. Developers and coders can align their tasks with the overall project timeline, ensuring that software development and integration phases are synchronized with construction milestones. This synchronization enhances project predictability and allows for more effective resource allocation.
Efficient Clash Detection and Issue Resolution
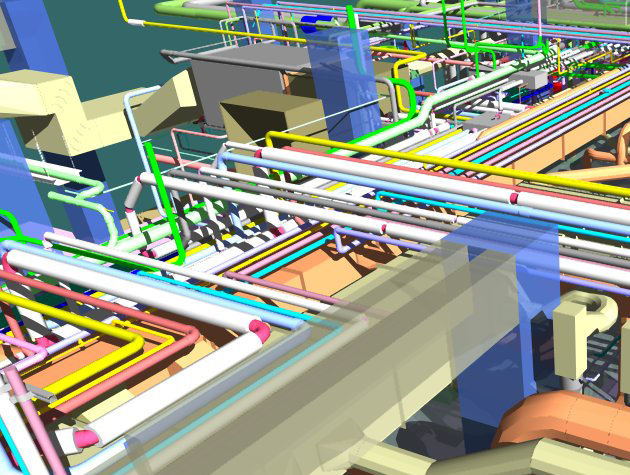
In traditional construction processes, clashes and conflicts among different building components often arise during the construction phase, leading to rework and delays. BIM addresses this challenge by facilitating clash detection in the virtual environment before construction begins.
Developers and coders can leverage clash detection tools within the BIM software to identify potential conflicts between architectural, structural, and systems elements. By resolving these issues in the digital realm, developers can preemptively adjust their code to accommodate necessary changes, saving time and resources during the construction phase.
Cost and Resource Optimization
BIM's ability to provide a comprehensive view of a project extends beyond its design and construction phases. Developers and coders can utilize the data-rich BIM model to analyze and optimize the long-term operational and maintenance costs of a building.
By incorporating information about the materials, components, and systems used in a structure, developers can create software solutions that contribute to energy efficiency, predictive maintenance, and resource optimization. This holistic approach aligns with the growing emphasis on sustainable and smart building practices, positioning developers and coders at the forefront of innovation.
Automated Code Generation and Maintenance
BIM can be a game-changer for developers by automating certain aspects of code generation and maintenance. With a detailed BIM model as a reference, developers can write scripts or use automated tools to generate code that corresponds to the building's elements and functions.
This not only accelerates the coding process but also ensures accuracy and consistency across the software components. Additionally, when updates or modifications are made to the building design, the corresponding code can be automatically adjusted, reducing the manual effort required for maintenance.
Augmented and Virtual Reality Integration
The integration of BIM with augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) technologies opens new avenues for developers and coders. BIM models can be overlaid onto the physical construction site using AR, allowing developers to visualize how their software interfaces with the real-world environment.
Similarly, VR can be employed for immersive simulations, enabling developers to experience the building's design in a virtual space. This not only enhances the understanding of project requirements but also facilitates iterative testing and refinement of software interfaces before deployment.
Challenges and Considerations
While the adoption of BIM in the construction industry presents numerous benefits, developers and coders should be mindful of certain challenges and considerations.
Learning Curve and Skill Acquisition:
Implementing BIM requires a learning curve for both construction professionals and developers. Developers need to familiarize themselves with BIM software and its specific requirements. Additionally, collaboration between architects, engineers, and coders may necessitate a shared understanding of each discipline's language and processes.
To overcome this challenge, developers can invest in training programs and collaborative workshops that bridge the knowledge gap between construction and software development. This mutual understanding is crucial for successful interdisciplinary collaboration.
Data Interoperability and Standards:
The effectiveness of BIM relies on seamless data interoperability between different software applications and platforms. Developers and coders must adhere to industry standards and protocols to ensure that their software can integrate seamlessly with BIM models.
Establishing common data exchange standards enables interoperability, making it easier for developers to create applications that can communicate with various BIM platforms. By prioritizing standardized data formats and protocols, developers contribute to a more cohesive and interconnected construction ecosystem.
Security and Data Privacy:
BIM involves the creation and management of extensive datasets containing sensitive information about building designs, components, and systems. Developers must prioritize the implementation of robust cybersecurity measures to protect this valuable data from unauthorized access and potential breaches.
Encryption, access controls, and secure data transmission protocols are essential components of a comprehensive security strategy. Developers should collaborate with cybersecurity experts to ensure that their applications comply with industry best practices and regulations governing data privacy.
Adapting to Dynamic Project Requirements
Construction projects are dynamic, with design changes and modifications occurring throughout the project lifecycle. Developers and coders must be adaptable and responsive to these changes, as modifications in the building design may necessitate corresponding adjustments in the software code.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Geospatial World
Implementing agile development methodologies can help developers respond effectively to changing project requirements. Regular communication and collaboration between the development team and other project stakeholders are crucial to ensure that software solutions align with evolving design specifications.
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling has emerged as a transformative force in the construction industry, offering a collaborative and data-driven approach to building design, construction, and operation. Developers and coders play a crucial role in harnessing the potential of BIM, contributing to enhanced project efficiency, cost optimization, and sustainable building practices.
By embracing BIM, developers can participate in a more integrated and collaborative construction process, where their software solutions seamlessly align with the architectural and engineering aspects of a project.
As the construction industry continues to evolve, the synergy between BIM and software development becomes increasingly essential for driving innovation and shaping the future of construction projects. Through continuous learning, collaboration, and adherence to industry standards, developers and coders can position themselves at the forefront of this technological revolution, unlocking new possibilities for efficient and sustainable construction practices.
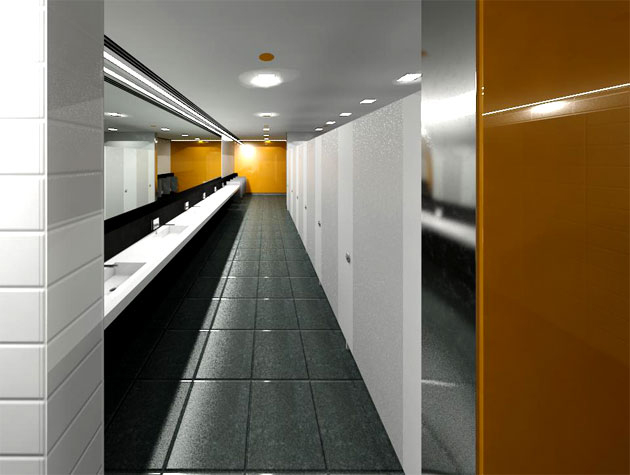
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !