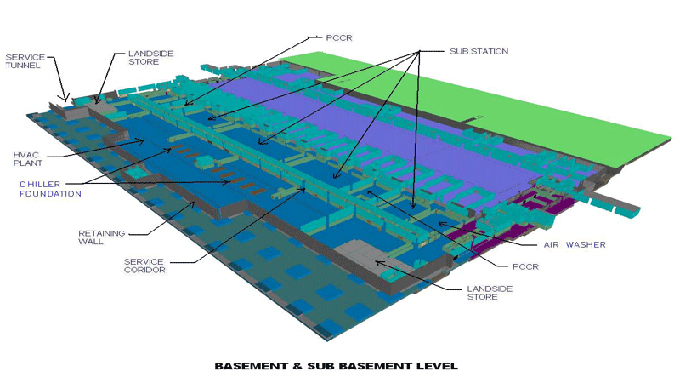
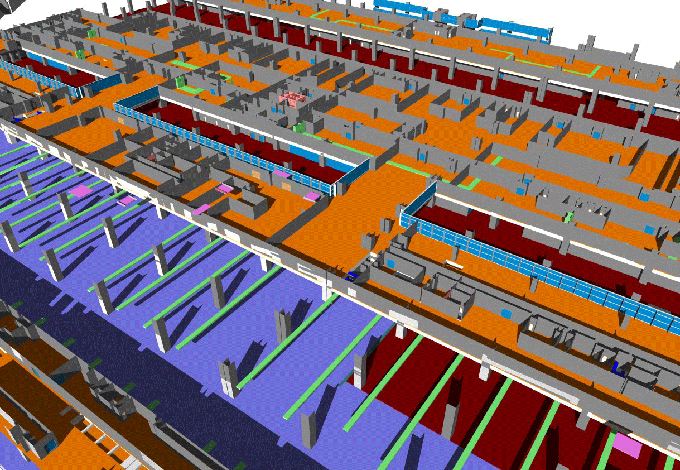
Innovating Construction: Building a Temporary Cabin House with BIM Technology
Tweet
In the realm of construction, the integration of technology has revolutionized traditional practices, paving the way for more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable solutions. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is at the forefront of this transformation, offering a comprehensive digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a structure.
Understanding BIM and Its Significance in Construction
A. What is BIM?
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a collaborative process that involves the creation and management of a digital representation of a building's physical and functional characteristics. This model becomes a shared knowledge resource for information about a facility, forming a reliable basis for decisions during its lifecycle.
B. Significance of BIM in Construction
1. Collaboration and Coordination: BIM fosters collaboration among various stakeholders, including architects, engineers, contractors, and project managers. This collaboration ensures better coordination and communication throughout the construction process.
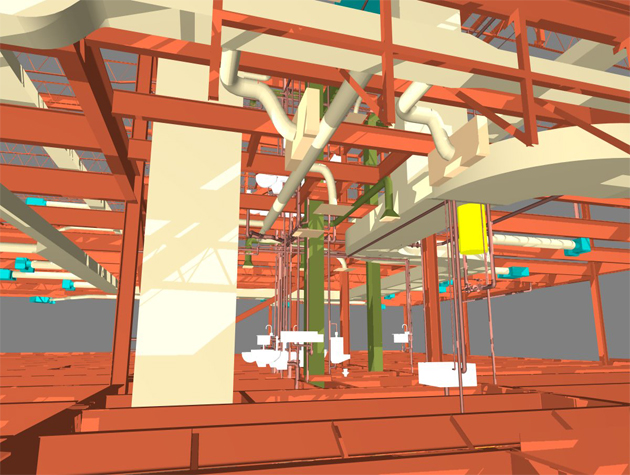
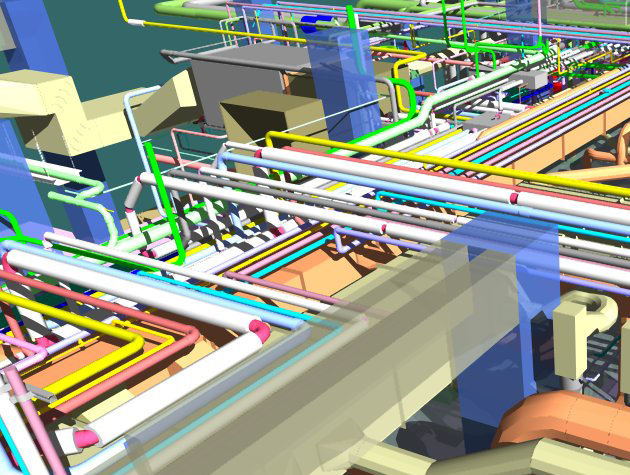
2. Visualization and Simulation: BIM allows stakeholders to visualize the entire project in 3D, facilitating better decision-making. It also enables simulation of construction processes, helping identify potential issues and optimize workflows.
3. Data-driven Decision-Making: BIM integrates data and information about the building, providing a foundation for informed decision-making. This data-driven approach enhances efficiency and reduces errors during the construction phase.
Temporary Cabin Houses: A Niche Application for BIM
A. Introduction to Temporary Cabin Houses
Temporary cabin houses serve a variety of purposes, ranging from construction site offices and emergency shelters to temporary residences. These structures require careful planning and execution, and BIM offers a unique set of advantages in this context.
B. Rapid Deployment and Mobility
Temporary cabin houses are often needed in remote locations or areas with limited infrastructure. BIM can streamline the design and planning process, allowing for rapid deployment and mobility as needed.
C. Cost-Effective Construction
BIM's ability to optimize resources and streamline workflows contributes to cost-effective construction. This is particularly valuable for temporary structures, where budget constraints often play a significant role.
BIM in the Design Phase of Temporary Cabin Houses
A. Conceptual Design and Visualization
1. Design Exploration: BIM facilitates multiple design iterations, allowing stakeholders to explore various concepts before finalizing the design. This is crucial for temporary cabin houses, where functionality and efficiency are paramount.
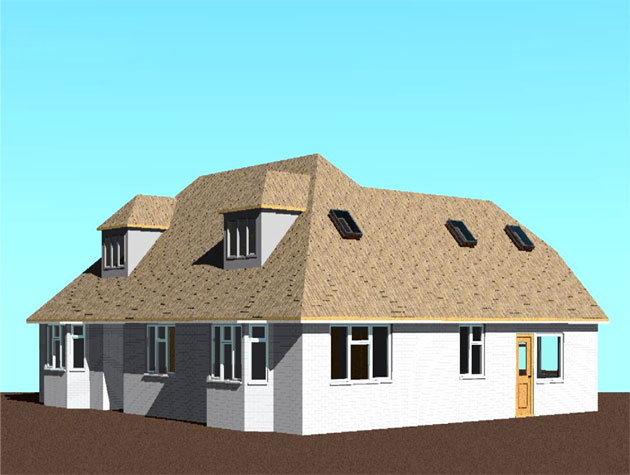
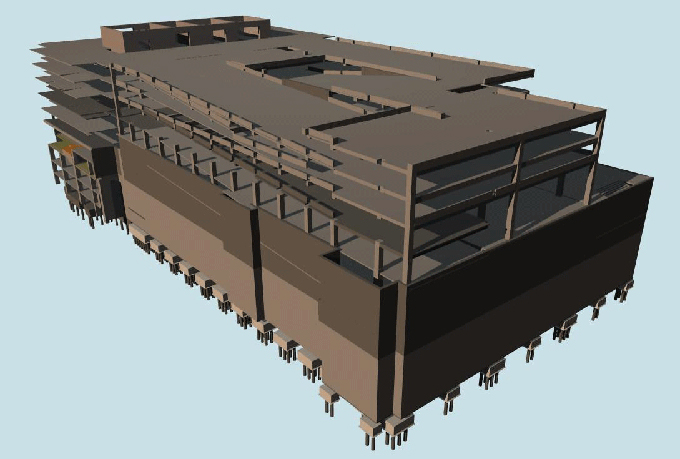
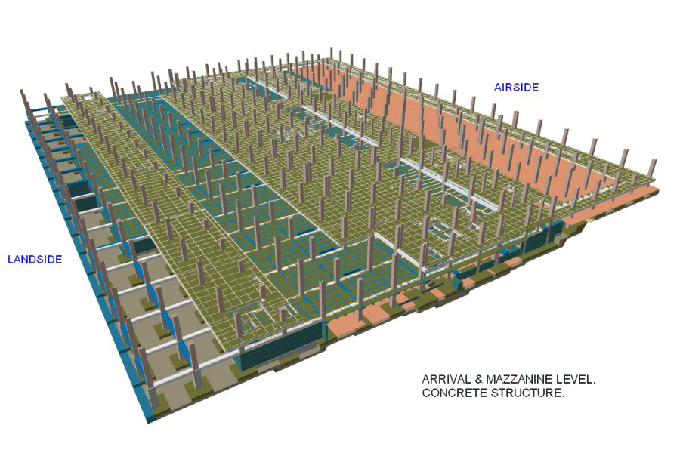
2. 3D Visualization: BIM's 3D modeling capabilities provide a realistic visualization of the temporary cabin house, helping stakeholders assess the design and make informed decisions.
B. Parametric Design and Flexibility
1. Parametric Modeling: BIM allows for parametric design, where parameters such as size, shape, and materials can be easily adjusted. This flexibility is advantageous in creating temporary structures that can be tailored to specific requirements.
2. Design Changes and Adaptability: As the needs for temporary cabin houses may evolve, BIM enables quick and efficient design changes, ensuring adaptability throughout the project lifecycle.
BIM in the Construction Phase of Temporary Cabin Houses
A. Prefabrication and Modular Construction
1. Prefabrication Benefits: BIM supports prefabrication by providing accurate and detailed digital models that can be used to manufacture components off-site. This reduces construction time and enhances precision.
2. Modular Construction: Temporary cabin houses often benefit from modular construction methods. BIM facilitates the design and coordination of modular components, ensuring seamless integration on-site.
B. Clash Detection and Construction Optimization
1. Clash Detection: BIM's clash detection capabilities identify potential conflicts in the construction process before they occur on-site. This minimizes rework and enhances overall construction efficiency.
2. Construction Sequencing: BIM allows for the simulation of construction sequences, optimizing the building process and ensuring that temporary cabin houses are erected in the most efficient and timely manner.
BIM in the Operation and Maintenance of Temporary Cabin Houses
A. Facilities Management and Lifecycle Information
1. As-Built Documentation: BIM provides accurate as-built documentation, ensuring that the facility's information is up-to-date. This is crucial for the operation and maintenance of temporary cabin houses, especially when modifications or expansions are necessary.
2. Asset Management: BIM serves as a comprehensive asset management tool, allowing stakeholders to track and manage components within the temporary cabin house throughout its lifecycle.
B. Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
1. Performance Analysis: BIM enables energy performance analysis, helping identify opportunities to enhance the energy efficiency of temporary cabin houses. This is essential for structures intended for long-term use.
2. Sustainable Materials and Practices: BIM supports the integration of sustainable materials and construction practices, aligning temporary cabin houses with environmentally friendly principles.
Challenges and Considerations
A. Initial Investment and Training
1. Cost of Implementation: While the long-term benefits are significant, there is an initial investment associated with implementing BIM technology. Stakeholders must carefully weigh the costs against the potential advantages.
2. Training and Skill Development: Adequate training for all stakeholders involved in the project is essential to harness the full potential of BIM. This includes architects, engineers, contractors, and facilities managers.
B. Interoperability and Collaboration
1. Standardization Challenges: The construction industry is still working towards standardizing BIM processes and formats. Interoperability challenges may arise when different stakeholders use varying software platforms.
2. Collaborative Culture: Successful BIM implementation requires a collaborative culture among project participants. Establishing effective communication channels is crucial for the seamless exchange of information.
Case Studies: Successful Implementation of BIM in Temporary Cabin House Construction
A. Emergency Shelter Project
1. Rapid Deployment: BIM facilitated the rapid deployment of emergency shelters in disaster-stricken areas, optimizing design and construction processes for quick and efficient assembly.
2. Adaptive Design: The parametric design capabilities of BIM allowed for adaptive design changes to meet the evolving needs of the affected population.
B. Construction Site Offices
1. Prefabrication and Modular Construction: BIM streamlined the construction of temporary site offices through prefabrication and modular construction methods, reducing overall construction time and costs.
2. Clash Detection: By identifying clashes in the design phase, BIM prevented on-site conflicts, minimizing disruptions and ensuring a smooth construction process.
Future Trends and Innovations
A. Integration with Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
1. AR for On-site Construction: The integration of BIM with AR allows on-site workers to visualize digital models in the real-world environment, improving accuracy and efficiency during construction.
2. VR for Stakeholder Engagement: VR technology enhances stakeholder engagement by providing immersive experiences, allowing clients and project teams to better understand and interact with the temporary cabin house design.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: ACCA software - EN
B. Cloud-Based Collaboration and Data Management
1. Cloud-Based BIM Platforms: The adoption of cloud-based BIM platforms facilitates real-time collaboration among dispersed project teams, improving communication and information sharing.
2. Data Analytics for Performance Monitoring: BIM's integration with data analytics enables continuous performance monitoring, allowing stakeholders to make data-driven decisions throughout the lifecycle of temporary cabin houses.
Conclusion
The integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology in the construction of temporary cabin houses signifies a paradigm shift in the way these structures are designed, built, and maintained. From the conceptual design phase to construction, operation, and maintenance, BIM offers a holistic approach that enhances efficiency, reduces costs, and ensures sustainability.
As the construction industry continues to evolve, embracing BIM in the context of temporary cabin houses opens up new possibilities for innovative and responsive solutions in various applications. The future promises further advancements, with emerging technologies like AR, VR, and cloud-based collaboration pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in temporary construction projects. Stakeholders who embrace and adapt to these technological trends stand to benefit from a more streamlined, resilient, and sustainable approach to building temporary cabin houses.

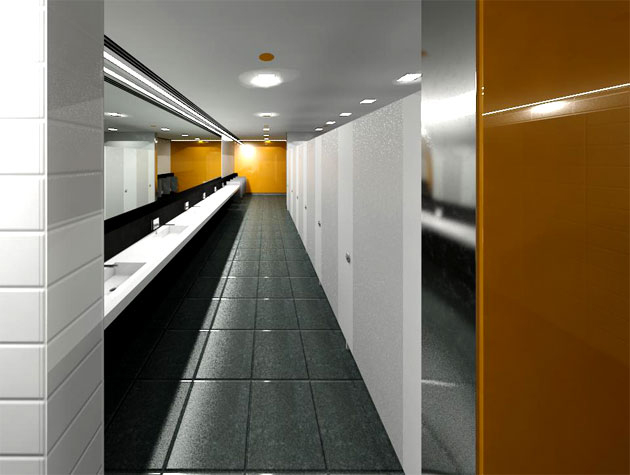
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !