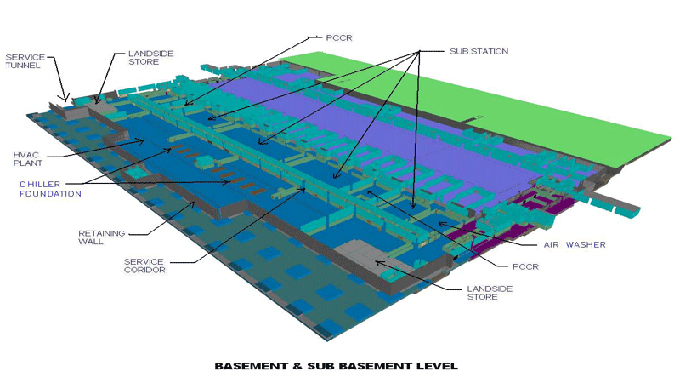
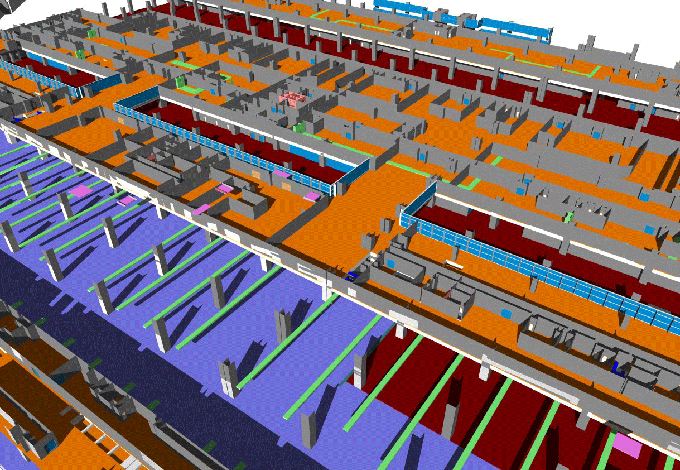
Building Movie Magic with BIM: Revolutionizing Movie Set Construction and Equipment Selection
Tweet
In the world of filmmaking, the creation of captivating movie sets and the selection of the right equipment are pivotal to the success of a production. The industry has long relied on creativity, craftsmanship, and technical expertise to bring stories to life on screen. However, in recent years, Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology has emerged as a game-changer in the process of making movie sets and choosing the perfect equipment.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore how BIM is revolutionizing the art of building movie sets and optimizing movie equipment selection.
Redefining Movie Set Construction with BIM
1. Conceptualizing and Designing Sets
Traditionally, the process of designing movie sets involved blueprints, sketches, and physical models. While these methods still play a crucial role, BIM adds a new dimension to the process.
Digital Visualization: BIM enables filmmakers to create digital 3D models of movie sets, allowing for immersive visualizations that provide a more accurate representation of the final product.
Collaboration: BIM facilitates collaboration among various departments, including set designers, production designers, and construction teams. It promotes efficient communication and reduces the risk of misinterpretations.
2. Set Construction Planning
Once the set design is finalized, BIM technology continues to streamline the construction phase.
Materials Selection: BIM software can assist in selecting the appropriate construction materials, taking into account factors like aesthetics, durability, and budget constraints.
Budgeting and Cost Estimation: BIM tools offer cost estimation features that help in accurate budgeting for set construction, reducing the likelihood of unexpected expenses.
3. Constructing the Set
During the construction phase, BIM enhances precision and efficiency.
Prefabrication: BIM allows for modular construction, enabling elements of the set to be prefabricated with high precision. This reduces on-site construction time and potential errors.
On-Site Management: Construction teams can access BIM models on-site via mobile devices, ensuring that the set is being built according to the design.
Clash Detection: BIM software can detect clashes or conflicts in the design, preventing issues that could arise during construction.
4. Safety and Compliance
Safety Planning: BIM can be used to plan safety measures on set, ensuring that all regulations and safety standards are met. It can help identify potential hazards in advance.
Leveraging BIM for Movie Equipment Selection
1. Camera and Equipment Planning
Selecting the right camera and equipment is crucial for capturing the director's vision effectively.
Camera Compatibility: BIM can help filmmakers assess which cameras are compatible with the chosen set and its dimensions. It ensures that the camera equipment fits seamlessly within the environment.
Camera Angles and Shots: BIM models can simulate camera angles and shots within the set, allowing for more precise planning of cinematography.
2. Sound and Lighting
BIM is not limited to visuals; it can also optimize sound and lighting equipment selection.
Acoustic Modeling: BIM can simulate acoustic properties within a set, aiding in the selection and placement of microphones and speakers for optimal sound quality.
Lighting Design: BIM allows for accurate lighting simulations, helping filmmakers choose the right lighting equipment and placements to achieve the desired mood and atmosphere.
3. Equipment Inventory and Maintenance
Inventory Management: BIM can be used to keep track of all movie equipment, ensuring that nothing is overlooked or misplaced during a shoot.
Maintenance Scheduling: BIM can automate maintenance schedules for equipment, reducing downtime due to unexpected malfunctions.
4. Post-Production Integration
Seamless Data Transfer: BIM technology can facilitate the seamless transfer of set and equipment data into post-production workflows. This integration ensures that post-production teams have accurate information for CGI integration and visual effects.
Case Studies: BIM in the Film Industry
Let's explore real-world examples of how BIM has been used in the film industry to create stunning sets and optimize equipment selection:
1. "Avatar" (2009)
Director James Cameron used BIM extensively for the creation of the fictional world of Pandora. BIM technology allowed for the visualization of intricate landscapes and structures, making the film's stunning visuals possible.
2. "The Great Gatsby" (2013)
Baz Luhrmann's adaptation of F. Scott Fitzgerald's classic novel featured lavish set designs from the Roaring Twenties. BIM helped recreate the grandeur of the era, from the opulent mansions to the vibrant streets of New York.
3. "Gravity" (2013)
The sci-fi thriller directed by Alfonso Cuarón relied on BIM for the meticulous planning of zero-gravity sequences. BIM simulations were used to choreograph camera movements and astronaut positions with utmost precision.
4. "The Mandalorian" (2019-Present)
The groundbreaking Disney+ series "The Mandalorian" utilized BIM and virtual production techniques to create immersive digital environments. BIM data was integrated into real-time virtual sets, enabling actors to perform against realistic digital backdrops.
The Future of BIM in Filmmaking
1. Virtual Production
BIM, combined with virtual production technologies like LED walls, is opening up new possibilities for filmmakers. It allows for the creation of dynamic, interactive virtual sets that respond to real-time camera movements.
2. Data-Driven Filmmaking
As BIM continues to evolve, it can provide filmmakers with valuable data insights. This data can be used to inform creative decisions, optimize production processes, and enhance the overall filmmaking experience.
3. Sustainability and Efficiency
BIM can contribute to sustainable filmmaking by optimizing resource use during set construction and equipment selection. It aids in reducing waste and energy consumption, aligning with environmentally conscious practices.
Challenges and Considerations
While BIM holds immense potential for the film industry, it is not without its challenges:
Cost: Implementing BIM technology requires investment in software, hardware, and training.
Workflow Integration: Integrating BIM into existing filmmaking workflows can be complex and requires adaptation.
Privacy and Security: Handling sensitive pre-production data with BIM raises privacy and security concerns that must be addressed.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Entertainment Partners
Conclusion
Building movie sets and selecting the right equipment are integral components of filmmaking. The advent of Building Information Modeling (BIM) technology has transformed these processes, making them more efficient, precise, and immersive. BIM empowers filmmakers to bring their visions to life with unprecedented accuracy and creativity.
As BIM continues to evolve and integrate with other cutting-edge technologies, it is poised to revolutionize the film industry even further. Filmmakers who harness the power of BIM will find themselves at the forefront of cinematic innovation, creating unforgettable movie sets and using equipment that enhances storytelling and visual artistry like never before.
The future of filmmaking is being shaped by the seamless marriage of technology and creativity, and BIM is at the heart of this cinematic revolution. With BIM, the magic of movie-making reaches new heights, captivating audiences around the world for generations to come.

Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !