The Transformative Power of BIM Tools in Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide
Tweet
In the world of architecture, staying ahead of the curve means embracing cutting-edge technologies that enhance efficiency, collaboration, and the overall quality of design and construction.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is one such technology that has revolutionized the architectural field. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the extensive use of BIM tools in architecture, their benefits, and the transformative impact they have on the industry.
Understanding Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Before delving into the applications and advantages of BIM in architecture, let's start with a clear understanding of what BIM is.
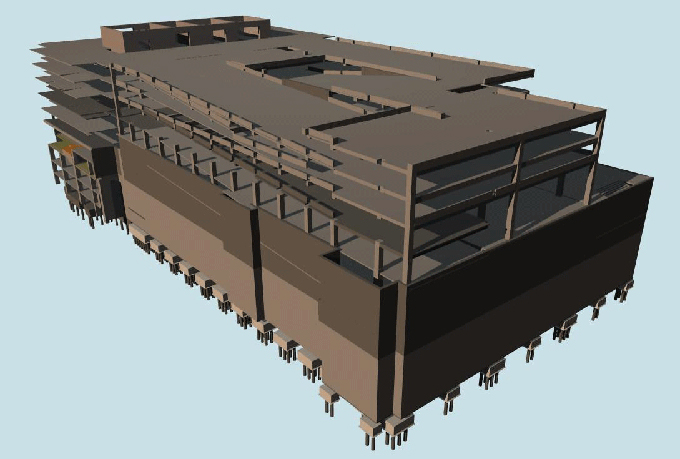
The Building Information Modeling (BIM) represents the physical and functional characteristics of a building digitally. It is a collaborative process that allows architects, engineers, construction professionals, and stakeholders to work together on a single, comprehensive model of a building throughout its entire lifecycle from design and construction to operation and maintenance.
Key Components of BIM
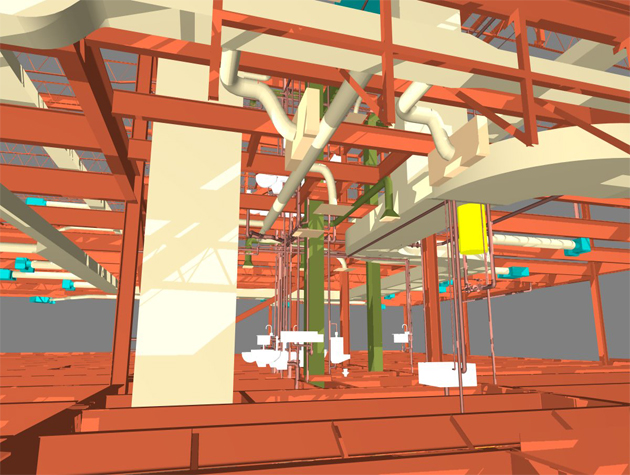
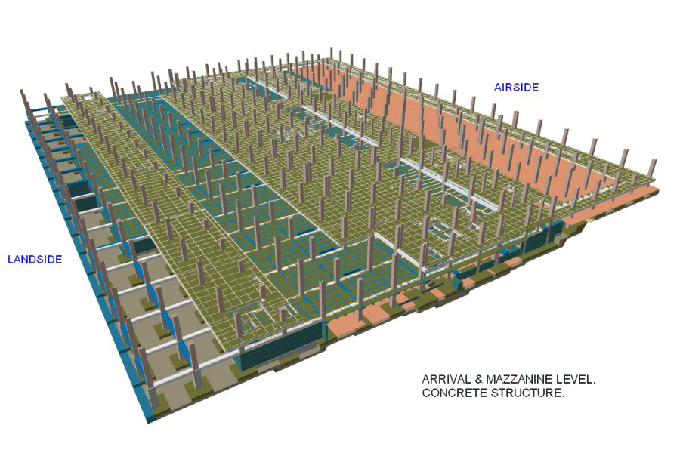
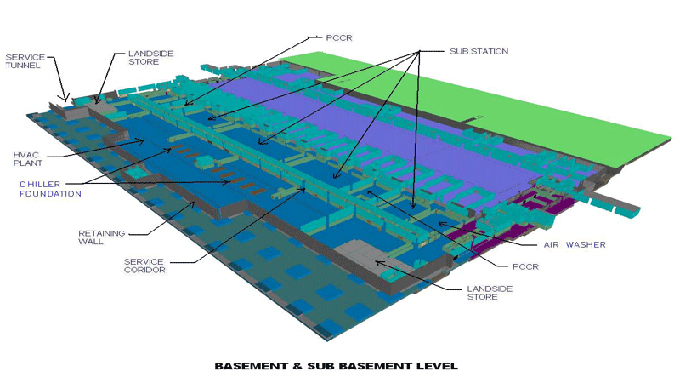
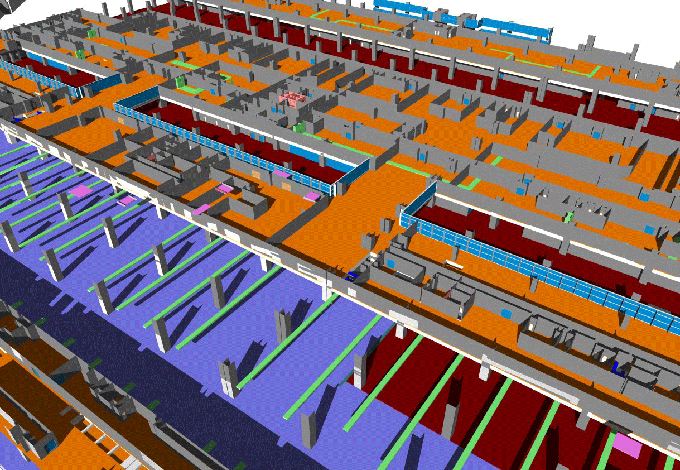
3D Modelling: BIM creates 3D models of buildings that include every detail, from structural components to interior finishes.
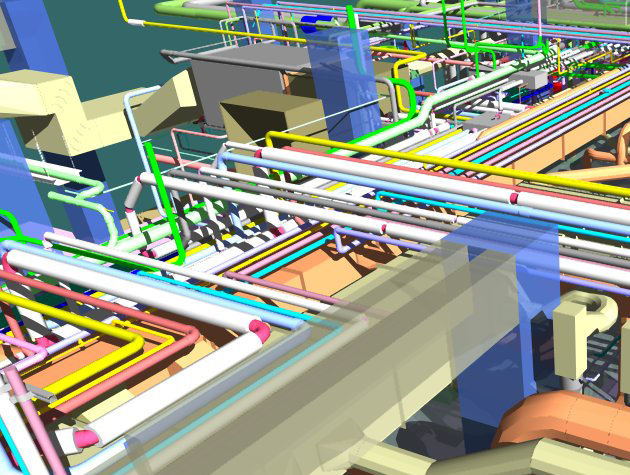
Data Integration: BIM integrates various data sources, including architectural, structural, mechanical, and electrical, into a unified model.
Collaboration: BIM facilitates collaboration among project stakeholders by providing a shared platform for information exchange.
Lifecycle Management: BIM supports the entire building lifecycle, from initial design to demolition, by capturing data on maintenance, renovations, and more.
The Role of BIM in Architectural Design
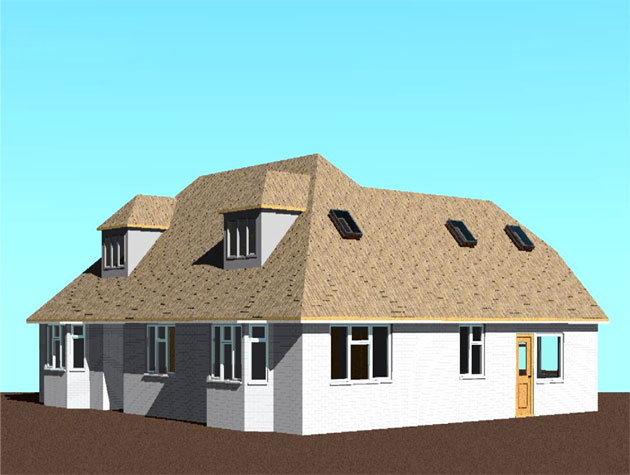
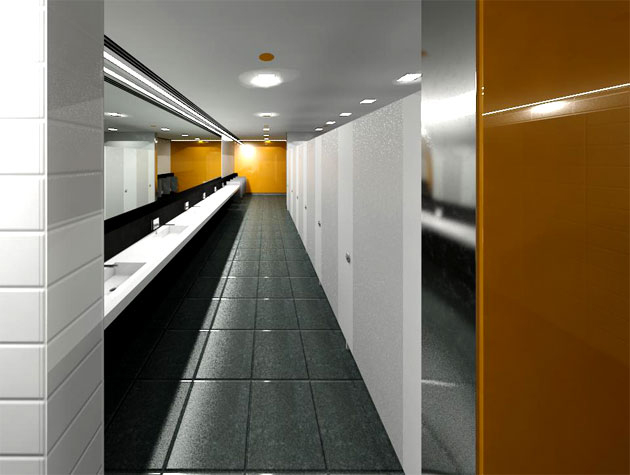
1. Visualization and Conceptualization BIM tools enable architects to create realistic 3D models of their designs, allowing clients and stakeholders to visualize the project better. This helps in making informed decisions about the design's aesthetics and functionality.
2. Design Development: Architects can use BIM to develop detailed design plans, analyze the impact of design choices, and ensure that the building's components are coordinated and integrated seamlessly.
3. Sustainability and Energy Analysis: BIM tools provide architects with the ability to perform energy simulations and analyze the environmental impact of design decisions. This supports the creation of sustainable and energy-efficient buildings.
4. Material Selection: BIM can assist in the selection of materials by providing detailed information on their properties, costs, and environmental impact. Architects can make informed choices that align with the project's goals.
The Construction Phase: BIM's Impact
1. Improved Accuracy: During construction, BIM models serve as a reference point for contractors. They provide accurate information on measurements, quantities, and materials, reducing errors and rework.
2. Construction Sequencing: BIM tools can help in visualizing the construction sequence. This aids in planning and scheduling activities, optimizing resources, and ensuring efficient construction progress.
3. Cost Estimation and Control: BIM facilitates cost estimation by providing detailed information on the project's components. It helps in monitoring costs throughout the construction phase, reducing the likelihood of budget overruns.
4. Clash Detection: BIM models can identify clashes or conflicts in the design, such as pipes running through structural elements. Early detection allows for corrective action before construction begins.
Post-Construction and Facility Management
BIM's utility extends beyond the construction phase. After a building is completed, BIM models continue to play a vital role in facility management and maintenance:
1. Operations and Maintenance: BIM models contain information about the building's systems and components. Facility managers can use this data for preventive maintenance, repairs, and asset management.
2. Renovations and Retrofits: When a building undergoes renovations or retrofits, BIM models provide a comprehensive understanding of the existing structure, making the planning and execution of such projects more efficient.
3. Space Management For organizations with large facilities, BIM can assist in space management by providing accurate information on space allocation and utilization.
4. Energy Performance Monitoring: BIM tools enable ongoing monitoring of a building's energy performance, helping facility managers make data-driven decisions to optimize energy usage.
The Benefits of BIM Tools in Architecture
The adoption of BIM tools in architecture offers numerous benefits that have a far-reaching impact on the industry:
1. Enhanced Collaboration: BIM promotes collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and other stakeholders. It provides a centralized platform for real-time information sharing, reducing communication gaps and conflicts.
2. Efficiency and Cost Savings: The use of BIM leads to increased efficiency in design, construction, and facility management. Fewer errors and rework translate to cost savings and reduced project timelines.
3. Improved Decision-Making: Architects can make informed decisions throughout the project lifecycle. BIM tools provide data-driven insights and supporting choices that align with the project's goals and requirements.
4. Sustainability: BIM contributes to sustainable building practices by enabling energy analysis, material selection, and environmental impact assessments. It encourages the design and construction of green and energy-efficient structures.
5. Risk Mitigation: The ability to detect clashes and conflicts early in the design phase minimizes risks during construction. This leads to a smoother construction process with fewer unexpected challenges.
6. Long-Term Value: BIM's value extends beyond the completion of a project. It supports facility management, renovations, and retrofits, ensuring that buildings maintain their functionality and value over time.
BIM Tools and Software
Several BIM tools and software platforms are widely used in the field of architecture. There are a number of popular ones, including:
Autodesk Revit: A comprehensive BIM platform specifically designed for architects and building professionals.
Graphisoft ArchiCAD: Known for its intuitive interface and advanced modelling capabilities.
Trimble SketchUp: While primarily known as a 3D modelling tool, SketchUp also offers BIM capabilities with extensions and plugins.
Nemetschek Vectorworks: Offers a versatile set of BIM tools suitable for architectural design and planning.
Bentley AECOsim: A BIM platform designed for large-scale and complex projects, often used in infrastructure and civil engineering.
Challenges and Considerations
While BIM offers numerous benefits, its implementation in architecture is not without challenges:
1. Initial Costs: Adopting BIM tools may require an initial investment in software, training, and hardware, which can be a barrier for some architectural firms.
2. Training and Skill Development: Architects and team members need training to become proficient in using BIM tools effectively.
3. Data Integration: Integrating data from different sources into a unified BIM model can be complex, requiring careful planning and coordination.
4. Data Security: Protecting sensitive project data is crucial. Architects must implement robust data security measures to prevent breaches.
5. Interoperability: Ensuring that BIM software and tools are compatible with other software used in the industry can be a challenge.
Future Trends in BIM for Architecture
The future of BIM in architecture is promising, with several trends on the horizon:
1. Cloud-Based BIM: Cloud-based BIM platforms offer greater flexibility, enabling collaboration from anywhere and on any device.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Tejjy Inc.
2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning are being integrated into BIM tools to automate tasks, optimize designs, and provide predictive analytics.
3. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): VR and AR are enhancing the visualization capabilities of BIM, allowing architects and clients to experience designs in immersive environments.
4. Sustainability and Performance Analysis: BIM tools are evolving to provide even more advanced sustainability analysis and performance simulations.
5. IoT Integration: The Internet of Things (IoT) is being integrated with BIM to enable real-time monitoring and control of building systems.
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) has transformed the field of architecture, offering architects and building professionals powerful tools to streamline design, construction, and facility management processes. BIM's ability to enhance collaboration, improve efficiency, and support sustainable building practices has made it an indispensable technology in the industry.
As architectural firms continue to adopt and adapt to BIM tools, they will not only benefit from cost savings and reduced risks but also contribute to the creation of smarter, more sustainable, and technologically advanced buildings that meet the demands of the modern world. In an ever-evolving industry, embracing BIM is not just a choice but a necessity for architects looking to excel and lead in the 21st century.
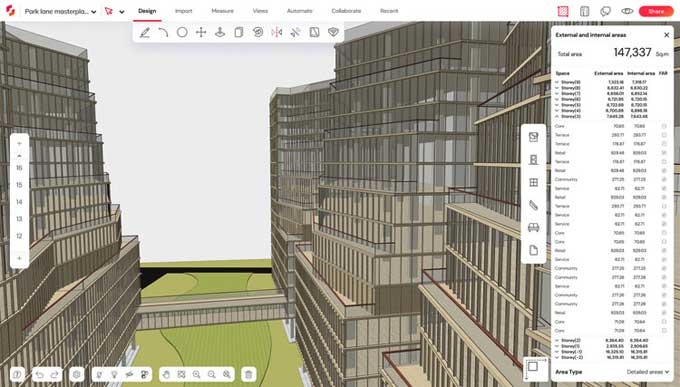
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !