Revolutionizing Food Manufacturing: The Role of BIM in the Food Industry
Tweet
The world of food manufacturing is undergoing a profound transformation, with technology playing a pivotal role in reshaping the industry. Building Information Modeling (BIM) is one such technology that has found an increasingly important role within the food industry.
An Overview of Building Information Modeling (BIM)
A building's physical and functional properties are digitally represented through Building Information Modeling (BIM). It is a collaborative process that enables stakeholders to plan, design, construct, and manage a building's lifecycle more efficiently.
BIM's Core Principles
BIM is built on several core principles:
1. Data Integration: BIM integrates data from various stakeholders and phases of a building's lifecycle, creating a comprehensive digital model.
2. Collaboration: It encourages collaboration among architects, engineers, contractors, and other parties, fostering better decision-making and problem-solving.
3. Visualization: BIM provides a 3D or 4D (time-based) visualization of a project, helping stakeholders understand complex concepts more easily.
4. Data Analysis: BIM allows for data analysis and simulation, enabling more informed decisions regarding a building's design, sustainability, and operation.
The Food Industry's Unique Challenges
Complexity of Food Facilities
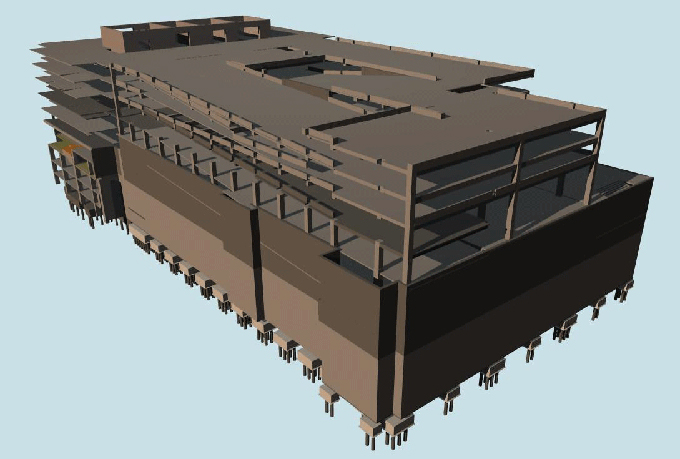
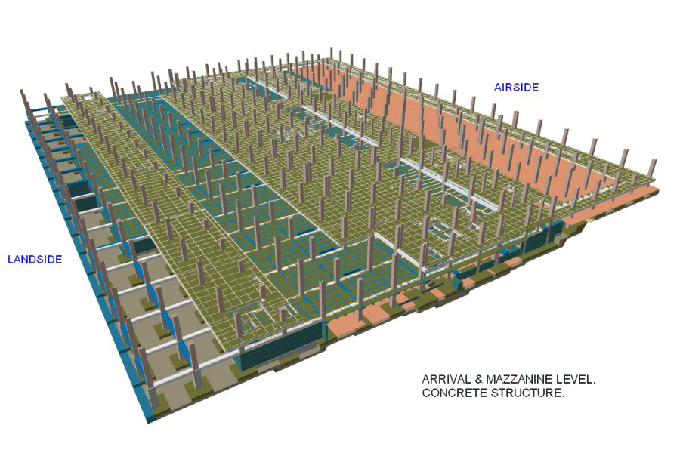
Food manufacturing facilities are known for their complexity. They must adhere to strict hygiene and safety standards while accommodating a variety of production processes and equipment. Designing and constructing such facilities require meticulous planning and a deep understanding of the industry's unique requirements.
Regulatory Compliance
The food industry is highly regulated, with stringent guidelines for food safety and quality. Meeting these standards is paramount, and any deviations can lead to severe consequences, including product recalls and damage to a company's reputation.
Sustainability and Efficiency
Modern consumers are increasingly concerned about sustainability and environmental impact. Food manufacturers are under pressure to reduce energy consumption, water usage, and waste production while still delivering high-quality products efficiently.
The Role of BIM in Food Manufacturing
Design and Visualization
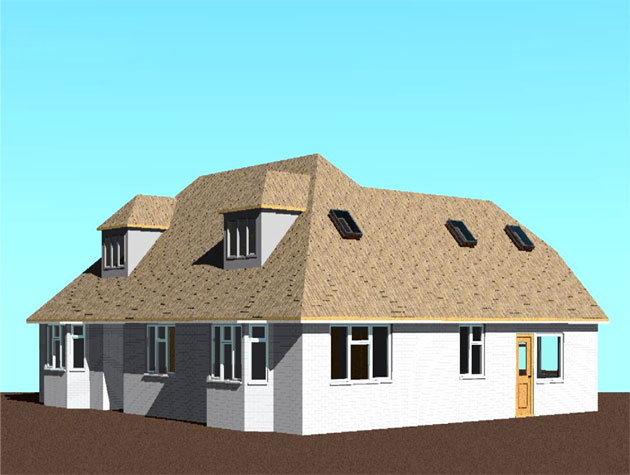
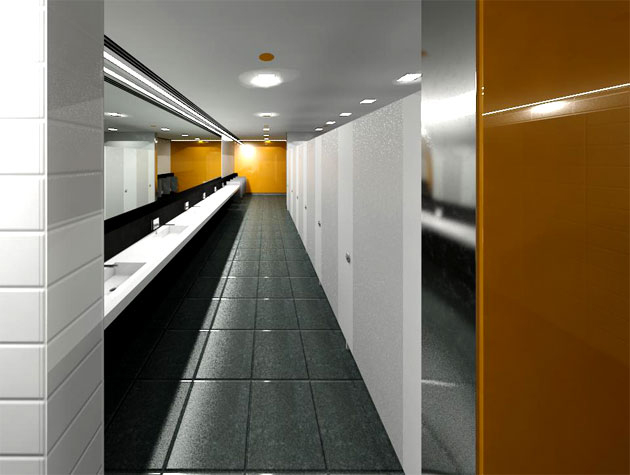
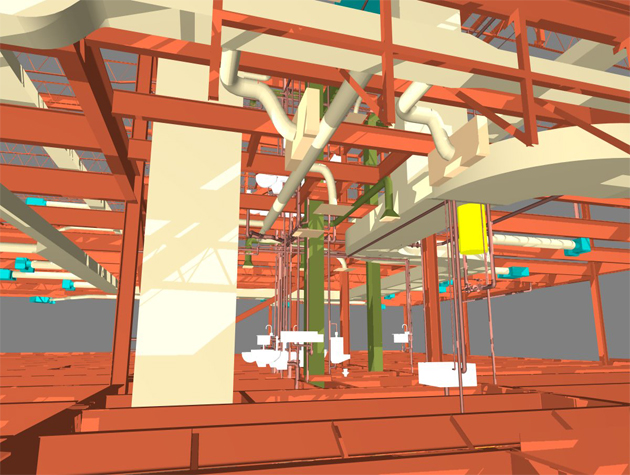
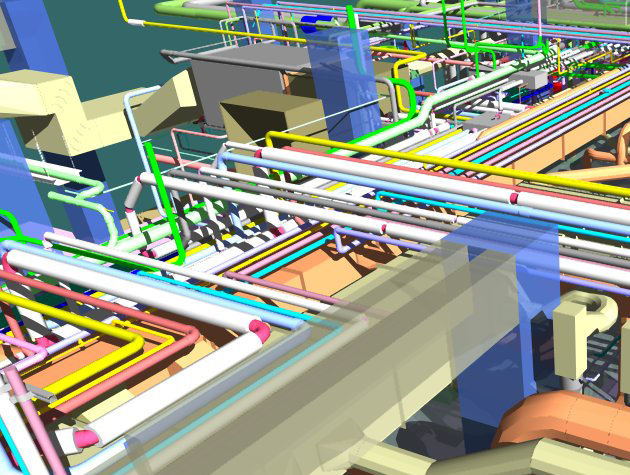
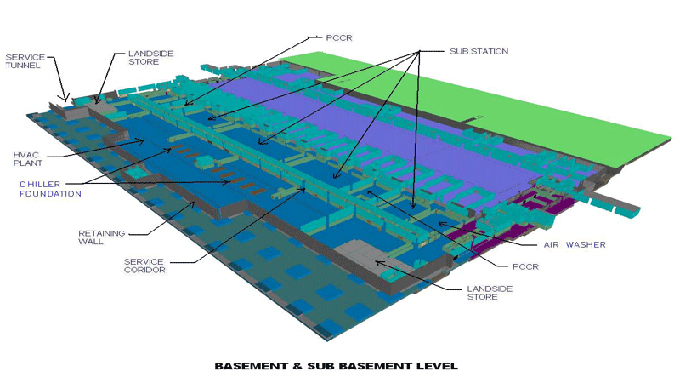
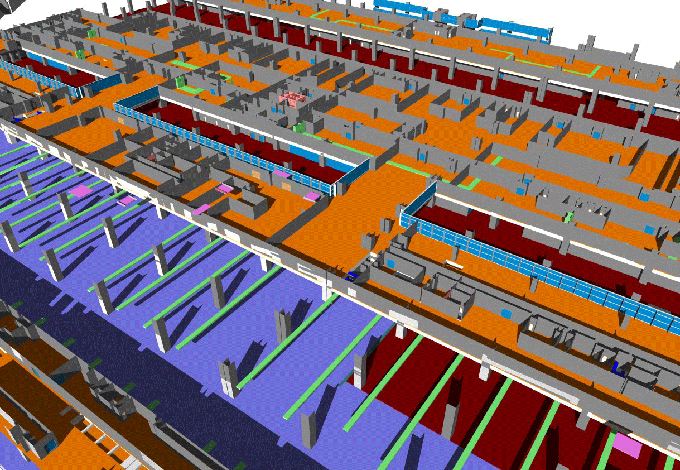
BIM provides food manufacturers with detailed, 3D models of their facilities before construction begins. This allows for thorough planning and visualization, which can reveal design flaws or inefficiencies early in the process.
Regulatory Compliance
BIM helps ensure that food manufacturing facilities meet the stringent requirements of regulatory bodies. It allows for precise planning of sanitation areas, waste management, and compliance with safety standards.
Energy Efficiency
Energy-efficient design is a crucial aspect of modern food manufacturing. BIM enables designers to model and analyze energy consumption and make informed decisions to reduce the environmental impact of facilities.
Workflow Optimization
BIM allows for better workflow optimization within food facilities. It aids in planning the arrangement of equipment, workflow processes, and personnel movement, which can lead to increased productivity and efficiency.
Case Studies - BIM in Action
1. Coca-Cola's Sustainable Bottling Plant
Coca-Cola's commitment to sustainability led to the creation of its first LEED-certified bottling plant. BIM played a crucial role in optimizing the facility's energy and water usage, waste management, and ensuring compliance with strict environmental standards.
2. Nestlé's Food Processing Plant
Nestlé, one of the world's largest food companies, utilized BIM in the construction of its food processing plant. This helped the company design a facility that met regulatory requirements, optimized production processes, and reduced energy consumption.
3. Brewery Modernization
Many breweries have turned to BIM to modernize their facilities. By modeling equipment placement and workflow, they can produce high-quality beer while reducing energy and water consumption.
Advantages of BIM in Food Manufacturing
1. Cost Savings
BIM reduces costly design errors and change orders, ultimately saving money in the construction process.
2. Improved Efficiency
The optimization of processes and workflow within food facilities leads to increased efficiency and higher production.
3. Sustainability
BIM helps in designing more sustainable facilities by optimizing energy and resource usage.
4. Regulatory Compliance
Precise planning and modelling ensure that food facilities meet stringent regulatory requirements.
5. Enhanced Safety
BIM aids in identifying and mitigating safety risks, which is paramount in food manufacturing.
Challenges and Limitations
1. Initial Investment
Implementing BIM requires a significant initial investment in technology and training, which can be a barrier for smaller food manufacturers.
2. Data Security
The digital nature of BIM models necessitates robust data security measures to protect sensitive information.
3. Learning Curve
Transitioning to BIM can be challenging, requiring a learning curve for employees and project stakeholders.
The Future of BIM in the Food Industry
The use of BIM in the food industry is expected to continue to grow. As technology advances and more success stories emerge, food manufacturers will increasingly adopt BIM as a standard practice. This will lead to more sustainable, efficient, and compliant food facilities.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: DESCON Structures Engineering BIM_3D-5D
Conclusion
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is a transformative technology that is reshaping the food manufacturing industry. It offers innovative solutions to the complex challenges of designing, constructing, and operating food facilities.
With BIM, food manufacturers can create more efficient, sustainable, and compliant facilities, setting the stage for a brighter and more environmentally conscious future in the food industry.

Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !