A Comprehensive Guide to Drafting Detailed Cost Estimates with BIM Software in Construction
Tweet
In the ever-evolving landscape of the construction industry, precision in cost estimation is paramount. Building Information Modeling (BIM) software has emerged as a revolutionary tool, not only for design and visualization but also for creating detailed and accurate cost estimates.
I. The Evolution of Cost Estimation in Construction
Traditional vs. BIM-Based Cost Estimation
Traditional cost estimation methods often rely on 2D drawings and manual calculations. While these methods have been foundational in the industry, they have limitations in capturing the complexities of modern construction projects. BIM-based cost estimation, on the other hand, leverages the three-dimensional intelligence of BIM models to provide a more accurate and holistic representation of the project.
Benefits of BIM-Based Cost Estimation:
a. Accuracy and Precision
BIM software allows for the creation of detailed 3D models that incorporate precise geometric and material data. This information significantly improves the accuracy of cost estimates compared to traditional methods.
b. Real-time Collaboration
BIM fosters real-time collaboration among project stakeholders. This collaborative environment ensures that all parties are working with the most up-to-date information, minimizing discrepancies and streamlining the cost estimation process.
c. Visualization and Analysis
The visual nature of BIM models enhances the ability to analyze and understand the project. Stakeholders can explore the virtual representation of the construction, making it easier to identify potential cost drivers and optimize resources.
d. Change Management
BIM facilitates efficient change management by allowing stakeholders to visualize the impact of design changes on cost estimates. This proactive approach helps in making informed decisions that align with budget constraints.
II. Preparing for BIM-Based Cost Estimation
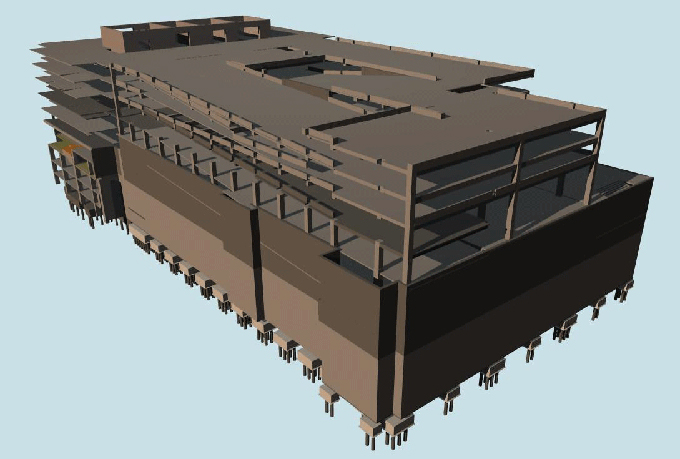
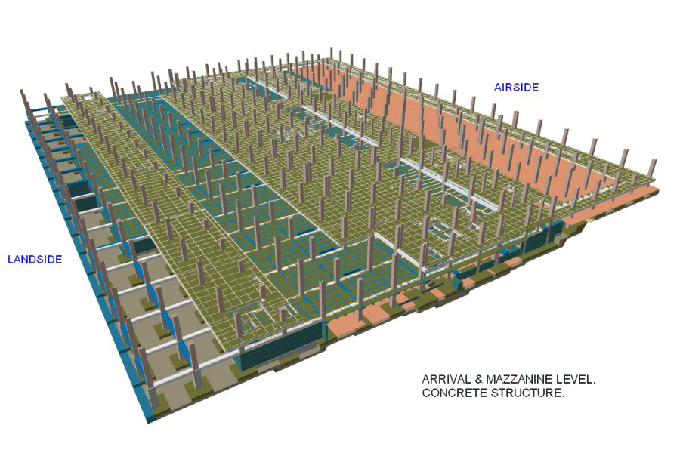
Create a Detailed BIM Model:
a. Include all Project Components
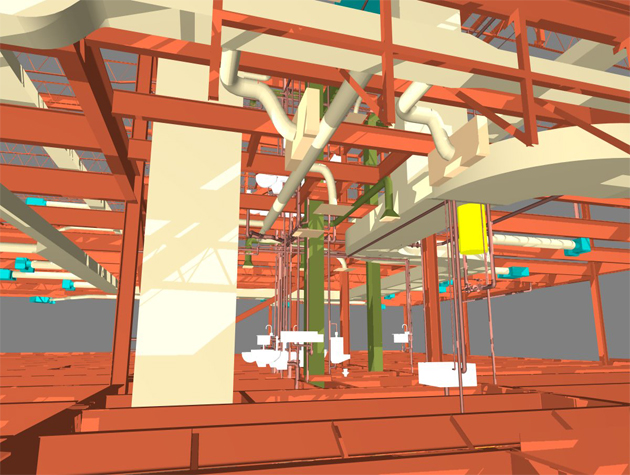
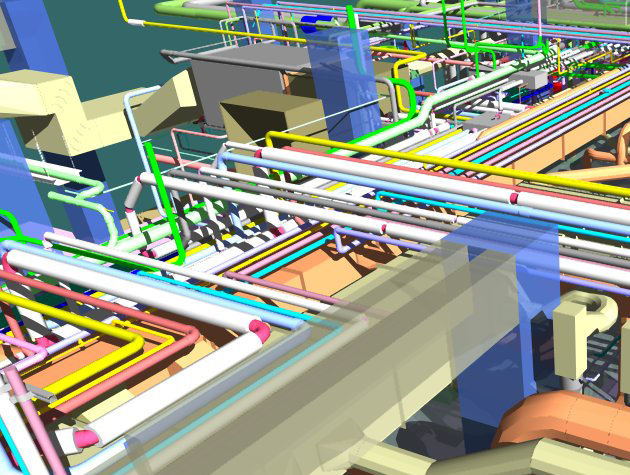
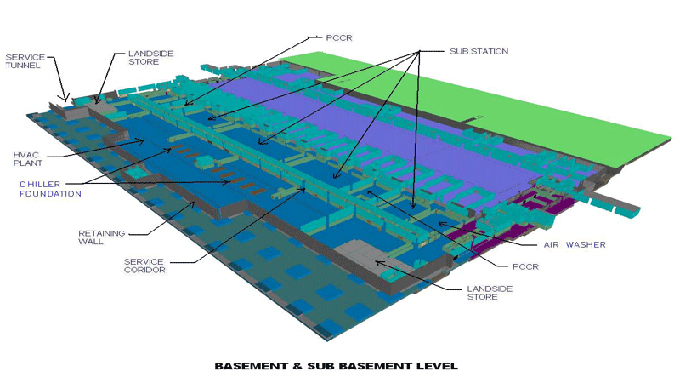
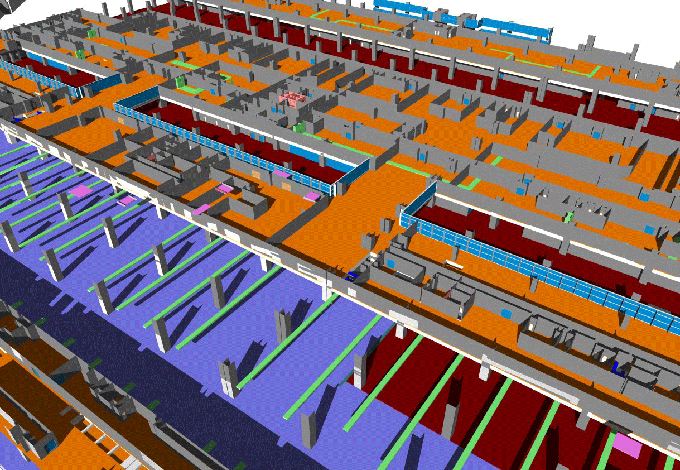
The BIM model should encompass all project components, from structural elements to MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) systems. This comprehensive representation forms the foundation for accurate cost estimation.
b. Define Materials and Quantities
Assign accurate material properties to elements in the model. This includes specifying the type, quantity, and cost of materials used in each component. BIM software allows for detailed material take-offs, ensuring a precise estimate.
Establish Cost Data Libraries:
a. Compile Unit Costs
Develop a comprehensive library of unit costs for various construction activities. This library should reflect current market rates for labor, materials, and equipment. These unit costs serve as the basis for estimating the cost of specific elements in the project.
b. Regularly Update Cost Data
Market conditions and costs fluctuate. Regularly updating the cost data library ensures that estimates are based on the most current and relevant information. This proactive approach contributes to the accuracy of the overall cost estimation process.
III. Step-by-Step Process of Drafting a Detailed Cost Estimate with BIM Software
Initial Setup:
a. Define Project Parameters
Input project-specific parameters such as location, project duration, and other relevant details. These parameters influence factors like labor costs and material availability, ensuring that the estimate is tailored to the project's unique context.
b. Import BIM Model
Import the detailed BIM model into the cost estimation software. BIM software such as Revit, ArchiCAD, or Tekla Structures facilitates the seamless integration of 3D models into the cost estimation process.
Element Identification and Quantification:
a. Break Down the Model
Break down the BIM model into individual components, including walls, floors, ceilings, and MEP systems. This breakdown allows for a detailed analysis of each element's cost contribution.
b. Quantify Materials
Leverage the BIM software's quantity take-off capabilities to quantify the materials required for each element. This involves extracting data on dimensions, volumes, and other relevant parameters.
Assign Unit Costs:
a. Refer to Cost Data Libraries
Use the established cost data libraries to assign unit costs to materials and construction activities. This step involves associating each material and labor activity with its corresponding unit cost from the library.
b. Consider Location-specific Factors
Adjust unit costs based on location-specific factors such as labor rates, material availability, and local regulations. This localization ensures that the estimate aligns with the economic conditions of the project site.
Labor and Equipment Costs:
a. Define Labor Requirements
Specify the labor requirements for each construction activity. This involves considering factors such as skill levels, productivity rates, and work hours. BIM software allows for the integration of labor data with the 3D model.
b. Incorporate Equipment Costs
If specialized equipment is required for certain activities, include the associated costs. BIM software facilitates the visualization and analysis of equipment usage within the context of the overall project.
Overhead and Contingency:
a. Include Overhead Costs
Factor in overhead costs, such as administrative expenses, project management fees, and general project overhead. These costs contribute to the overall project budget and are often expressed as a percentage of the total construction cost.
b. Allocate Contingency
Contingency allowances account for unforeseen circumstances or changes in project scope. BIM software enables stakeholders to visualize and allocate contingency funds where needed, enhancing risk management in the cost estimation process.
Finalizing the Estimate:
a. Review and Validate Data
Conduct a thorough review of the cost estimate. Validate data accuracy, ensure that all components are accounted for, and verify that unit costs align with current market rates.
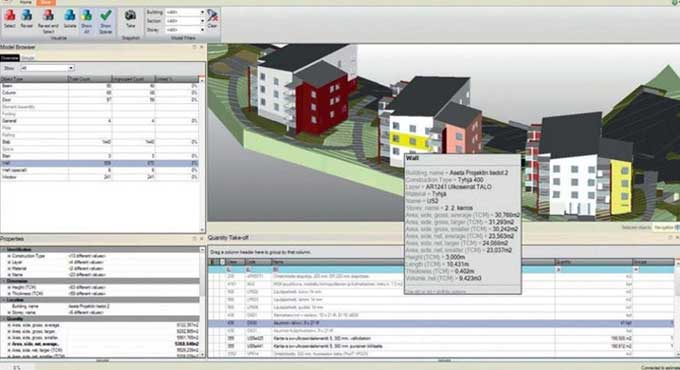
b. Generate Reports
BIM software allows for the generation of detailed reports and visualizations. These reports can include cost breakdowns by category, graphical representations of cost distribution, and other insights to aid decision-making.
IV. Challenges and Considerations in BIM-Based Cost Estimation
Data Accuracy and Integration:
a. Reliance on Accurate Data
The accuracy of BIM-based cost estimation is contingent on the accuracy of the input data. Inaccuracies in the BIM model or outdated cost data can lead to discrepancies in the estimate.
b. Integration Challenges
Achieving seamless integration between BIM software and cost estimation tools may present challenges. Stakeholders must ensure that data flows smoothly between the 3D model and the estimation software.
Training and Skill Requirements:
a. Skill Gap Challenges
The effective use of BIM software for cost estimation requires a certain level of expertise. Construction professionals may need training to acquire the skills necessary for proficient utilization of these tools.
b. Continuous Learning
Given the rapid evolution of BIM technology, construction professionals must engage in continuous learning to stay abreast of updates and new features that enhance the capabilities of cost estimation software.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: CYPE Software EN
Collaboration and Communication:
a. Interdisciplinary Collaboration
BIM-based cost estimation involves collaboration between various disciplines, including architects, engineers, and estimators. Clear communication channels and collaborative workflows are essential for successful interdisciplinary collaboration.
b. Client Communication
Communicating cost estimates effectively to clients is crucial. BIM software can facilitate client communication by providing visualizations that help clients understand the cost implications of design decisions.
Embracing Precision for Project Success
In the dynamic world of construction, where precision and accuracy are paramount, BIM-based cost estimation stands out as a transformative tool. By harnessing the power of 3D modeling, accurate data libraries, and collaborative workflows, construction professionals can create detailed and reliable cost estimates that serve as the foundation for successful project outcomes.
As the construction industry continues to embrace technological advancements, the integration of BIM software in cost estimation processes is not just a best practice , it is a strategic imperative for those seeking to thrive in the modern construction landscape.
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !