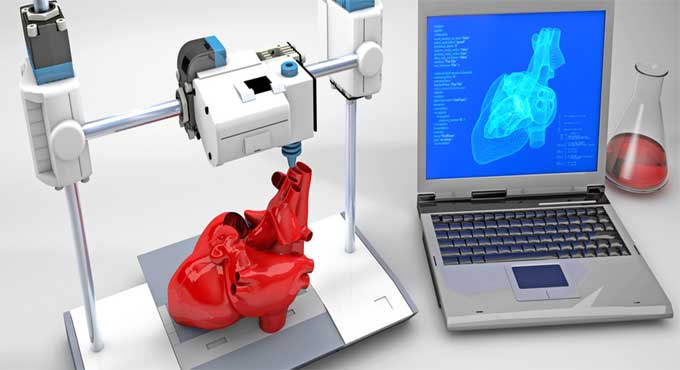
What does 3D Printing and 3D Bio-printing have to do with Healthcare?
Tweet
The medical industry has shown genuine interest in the advancement of 3D printing technology. A patient's specific anatomy can be used to print prosthetics and plastic dentures. A growing number of metal 3D printers are also attracting attention from manufacturers of medical tools, since they use actual metal powder filament instead of plastic colored metal. The most recent development, 3D bio-printing, is even more revolutionary.
For making living organs and tissues, bioprinting engineers use bio-inks instead of filaments such as plastic and metal. It is obvious that 3D printing and bio-printing would play an important role in the medical world concern patient treatments, such as prosthetics, dental work, surgical preparation, drug testing, and disease modeling.
3D Printed Prostheses
Prostheses made with the conventional manufacturing process tend to be expensive and uncomfortable unless they are done with surgical precision. It is more cost effective and promises higher accuracy to use 3D printing with help from a prosthetic company.
An artificial body part designed for comfort can be tailored made using a combination of a 3D scanner and a 3D printer.
High strength filaments have also been developed for 3D printing. Injured victims of natural disasters or war refugees have benefited from 3D printed prosthetics. As well as providing hope for patients' quality of life, the technology ensures that it is within their reach.
Surgical Preparation
3D scanners are as accurate as x-rays, MRIs, and CT scans when replicating patient specific organs. A STL file can be generated from the resulting image, which can then be printed. It is easier to prepare for surgery with an artificial organ. Before the procedure, doctors can examine superficial details like deformations or fractures using the artificial organ. The procedure is faster and less traumatizing for the patient as a result.
3D printed organs can also repair fractures and cracks, as well as repair spinal injuries and transplant organs. A 3D printed part can be used as a patient-specific mockup organ that surgeons can use to better understand the exact patient's anatomy. By preparing well, you can increase your chances of success and save time and money.
Drug Testing
The ability to test drugs ethically was another potential advantage of 3D bio-printing. The printed tissues share the same tissues as organic tissues, so researchers and doctors should be able to study diseases without using humans or animals. In the laboratory, organs can be observed, diseases can be monitored, and different treatment methods can be tested.
By administering the active chemicals of any medication to tissue, pharmaceutical companies can test a variety of drugs without involving human or animal subjects. Real-time testing with artificial and organic tissues pushes the boundaries of conventional drug testing procedures and generates more comprehensive data.
Medical Devices & Tools
With the help of a medical product design expert, metal powder filament can be used to make medical devices and even surgical tools quickly. It may not be of much use in a large city in a developed country, but it can be extremely valuable in rural medical facilities. A metal 3D printer can build a brand new tool within a day or less, saving doctors in hard to reach regions from waiting days or weeks for a replacement tool.
3D Printed Dental Applications
For dentists and patients alike, 3D printing services are invaluable. In today's world, braces, dental bridges, and denture frameworks can be fabricated without sacrificing accuracy. Molds are unnecessary because the dentist can manufacture all those features.
Technicians can easily install 3D printers in dental offices, clinics, and laboratories due to their small size. Although the equipment requires a substantial initial investment, it will pay for itself sooner rather than later with all the improvements it brings. The key to success in restoring teeth is precision, and well designed features for every patient optimize the chance of an ideal fit every time.
Disease Model of Cancer
Throughout the past 50 years, oncology treatments have made great strides in their effectiveness. The percentage of people who survived five years after being diagnosed with cancer increased from 50% in the 1970s to close to 70% in 2009.
Life expectancy has increased as a result of faster diagnosis, surgical interventions, better medications, and therapeutic interventions. In spite of this, cancer remains the leading cause of death worldwide. 3D bio-printing is driven by the search for personalized yet less invasive cancer treatments, as well as the need for faster and more accurate diagnostics.
Microenvironment Solution
During the development of cancerous cells, they can interact with healthy cells in the body & affect their growth. It affects growth chemicals, vascular cells, and immune cells within the microenvironment.
A scaffold imitating the microenvironment can be replicated with high resolution 3D bio-printing technology. Simulating DNA growth in real time may not be a cure, but it allows a clearer understanding of how the cells multiply and grow.
Drug Screening
In the meantime, patients' cancer cells can be used to create printed organs for drug screening procedures until more effective treatments emerge. It is common for cancer drugs to be toxic, and every patient reacts to the substances differently. A more efficient and safer screening process is possible with 3D bio-printing.
To get online demonstration, watch the following video tutorial.
Video Source: Hello World HD
Tumor Angiogenesis
Doctors can use 3D bioprinted organs as sacrificial lambs to gain a better understanding of the disease. In addition to developing complex valves and channels, a microfluidic chip can mimic tumor vascularization as well. In the event that doctors are fully aware of these concepts, they can develop effective anti-metastasis treatments for all patients. Anti-metastasis medications have not yet proven effective.
Drug Discovery
Pharmaceutical companies use bio-printed tissues for drug testing, while doctors use disease modeling to understand cancer pathogenesis. New cancer medications have been discovered through the combination of both.
In the case of non communicable diseases, there is a path to a breakthrough, but the path is never easy. Medical research into any other condition can be conducted using 3D bio-printed organs.
Gallery
Feel free to contact us for BIM requirements. One of our representative will respond you within 24 Hours. Send us your projects requirement today and grow your project.
Explore More !